Quality Of Service Part 1
ADVERTISEMENT
Q
S
P
1
UALITY OF
ERVICE
ART
packetlife.net
Quality of Service Models
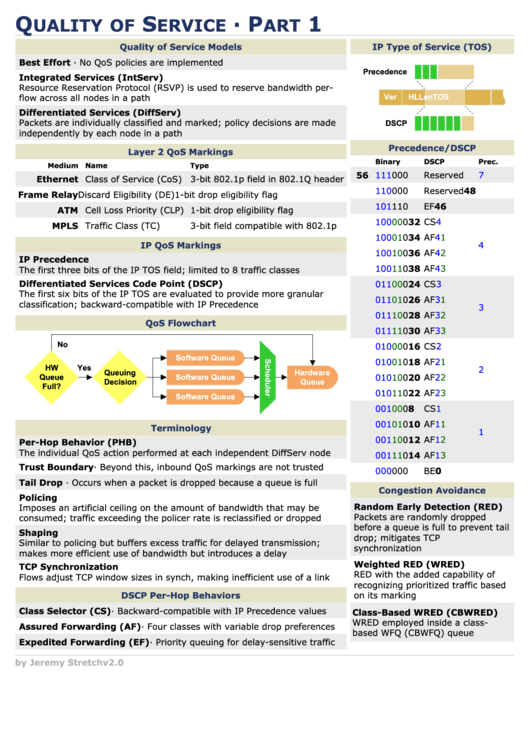
IP Type of Service (TOS)
Best Effort
No QoS policies are implemented
Precedence
Integrated Services (IntServ)
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) is used to reserve bandwidth per-
Ver
HL
TOS
Len
flow across all nodes in a path
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Packets are individually classified and marked; policy decisions are made
DSCP
independently by each node in a path
Precedence/DSCP
Layer 2 QoS Markings
Binary
DSCP
Prec.
Medium
Name
Type
56
111000
Reserved
7
Ethernet Class of Service (CoS)
3-bit 802.1p field in 802.1Q header
48
110000
Reserved
6
Frame Relay Discard Eligibility (DE) 1-bit drop eligibility flag
46
101110
EF
5
ATM
Cell Loss Priority (CLP)
1-bit drop eligibility flag
32
100000
CS4
MPLS
Traffic Class (TC)
3-bit field compatible with 802.1p
34
100010
AF41
IP QoS Markings
4
36
100100
AF42
IP Precedence
38
100110
AF43
The first three bits of the IP TOS field; limited to 8 traffic classes
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
24
011000
CS3
The first six bits of the IP TOS are evaluated to provide more granular
26
011010
AF31
classification; backward-compatible with IP Precedence
3
28
011100
AF32
QoS Flowchart
30
011110
AF33
No
16
010000
CS2
Software Queue
18
010010
AF21
HW
Yes
2
Queuing
Hardware
Queue
Software Queue
20
010100
AF22
Decision
Queue
Full?
22
010110
AF23
Software Queue
8
001000
CS1
10
001010
AF11
Terminology
1
12
001100
AF12
Per-Hop Behavior (PHB)
The individual QoS action performed at each independent DiffServ node
14
001110
AF13
Trust Boundary
Beyond this, inbound QoS markings are not trusted
0
000000
BE
0
Tail Drop
Occurs when a packet is dropped because a queue is full
Congestion Avoidance
Policing
Random Early Detection (RED)
Imposes an artificial ceiling on the amount of bandwidth that may be
Packets are randomly dropped
consumed; traffic exceeding the policer rate is reclassified or dropped
before a queue is full to prevent tail
Shaping
drop; mitigates TCP
Similar to policing but buffers excess traffic for delayed transmission;
synchronization
makes more efficient use of bandwidth but introduces a delay
Weighted RED (WRED)
TCP Synchronization
RED with the added capability of
Flows adjust TCP window sizes in synch, making inefficient use of a link
recognizing prioritized traffic based
DSCP Per-Hop Behaviors
on its marking
Class Selector (CS)
Backward-compatible with IP Precedence values
Class-Based WRED (CBWRED)
WRED employed inside a class-
Assured Forwarding (AF)
Four classes with variable drop preferences
based WFQ (CBWFQ) queue
Expedited Forwarding (EF)
Priority queuing for delay-sensitive traffic
by Jeremy Stretch
v2.0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








