Sample Care Plan Template Page 36
ADVERTISEMENT
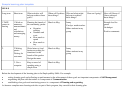
Nursing Diagnosis and Priority # 1
Impaired spontaneous ventilation R/T metabolic factors, 2/2 aspiration, 2/2 encephalopathy and right lower lobe airspace opacities
AEB patient ventilated (settings: TV-400, R-14, Mode-PRVC, FIO2-40, & PEEP-5), spike in BP above 200 systolic and 100 diastolic
with PVC/PAC ECG changes during sedation vacation, ABG values of 7.369, 101.7 (H), 57.8 (H), 32.6 (H), 6.2, & 97.4 and lactic
acid of 3.8, as well as shallow and diminished BS bilaterally in the bases.
General Goal:
Patient recovers and maintains a normal homeostasis for the remainder of shift after adverse hemodynamic episode that occurred
during sedation vacation.
Outcome Objective(s): (use SMART format)
1. The patient will maintain arterial blood gases within the following safe parameters a pH between 7.35 - 7.45, paco2 of 35-45 mm
Hg, hco3 of 22 to 26 mEq/liter, pao2 of 80 to 100 mm Hg, sao2 of 95% to 100%, and base excess of -5 to +3 during the nursing shift.
2. The patient’s airway will be effectively maintained during the nursing shift. The patient maintaining an sp02 above 95% will
measure an effect airway.
3. The nurse will aid the patient in effectively mobilizing secretions by performing inline suctioning as needed during the nursing
shift. The measurement of effective secretion mobilization is that the patient will not have adventitious lung sounds on auscultation.
Patient Responses
Interventions with time frames/frequency
Rationale (for each intervention)
(subjective/objective data)
1) Monitor the patient q2hrs for signs of
1) All of these assessment factors are signs
1) During the nursing shift the
increased respiratory rate, use of accessory
that the patient might not be tolerating the
patients respiratory status was
muscles, intercostal muscles retraction, flaring of
current ventilation settings and he could be
monitored for these signs q2hrs.
nostrils, and decreased 0
saturation (Ackley &
experiencing respiratory failure (Burns,
The patient did not experience any
2
Ladwig, 2011).
2005).
of this signs so his ventilation
settings are adequate and he is
tolerating the ventilator.
2) Administer analgesics and sedatives as needed
2) Studies have shown that when nurses
2) During the nursing shift (outside
of the patient’s adverse
to keep the patient comfortable while recovering
have a sedation protocol that allows them to
manage the patient’s analgesics and
from AWS (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011). Titrate up
hemodynamic reaction to his
and down within protocols to maintain
sedatives there is a decrease in the days of
sedation vacation) the patient
hemodynamics at stated parameters.
intubation and hospital stay (Brook et al.,
maintained his hemodynamic status
1999).
within stated parameters-systolic
F:\group\MEPN\MEPN Level III\NURS610B\2013NURS 610B\610BCarePlan
12/17/2012
page 16
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51