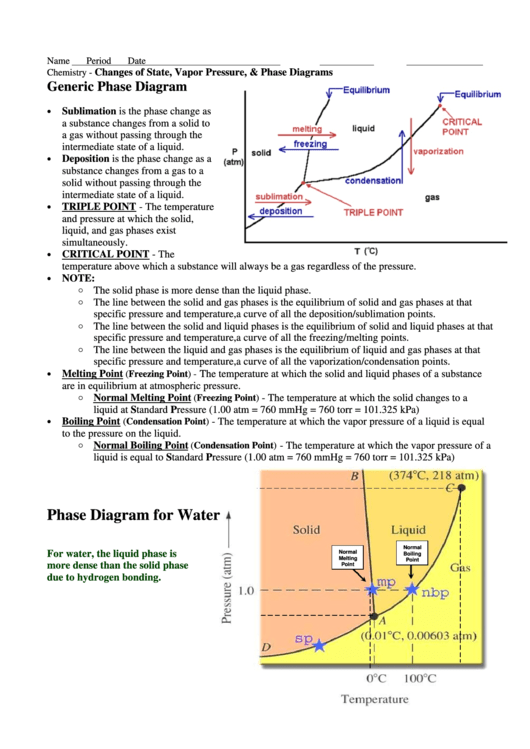
Chemistry - Changes Of State, Vapor Pressure, & Phase Diagrams Generic Phase Diagram
ADVERTISEMENT
Name
Period
Date
Changes of State, Vapor Pressure, & Phase Diagrams
Chemistry -
Generic Phase Diagram
•
Sublimation is the phase change as
a substance changes from a solid to
a gas without passing through the
intermediate state of a liquid.
•
Deposition is the phase change as a
substance changes from a gas to a
solid without passing through the
intermediate state of a liquid.
•
TRIPLE POINT - The temperature
and pressure at which the solid,
liquid, and gas phases exist
simultaneously.
•
CRITICAL POINT - The
temperature above which a substance will always be a gas regardless of the pressure.
•
NOTE:
The solid phase is more dense than the liquid phase.
o
The line between the solid and gas phases is the equilibrium of solid and gas phases at that
o
specific pressure and temperature, i.e. a curve of all the deposition/sublimation points.
The line between the solid and liquid phases is the equilibrium of solid and liquid phases at that
o
specific pressure and temperature, i.e. a curve of all the freezing/melting points.
The line between the liquid and gas phases is the equilibrium of liquid and gas phases at that
o
specific pressure and temperature, i.e. a curve of all the vaporization/condensation points.
•
Melting Point
The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a substance
(Freezing Point) -
are in equilibrium at atmospheric pressure.
Normal Melting Point
- The temperature at which the solid changes to a
(Freezing Point)
o
liquid at Standard Pressure (1.00 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 101.325 kPa)
•
Boiling Point
- The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal
(Condensation Point)
to the pressure on the liquid.
Normal Boiling Point
- The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a
(Condensation Point)
o
liquid is equal to Standard Pressure (1.00 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 101.325 kPa)
Phase Diagram for Water
Normal
For water, the liquid phase is
Normal
Boiling
Melting
Point
more dense than the solid phase
Point
due to hydrogen bonding.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4