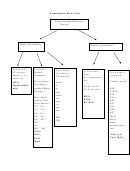
Rules Of Nomenclature And Nomenclature Flow Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
Rules of Nomenclature
Binary Ionic
Binary Molecular
Ternary Ionic
Acids (aqueous solutions)
(metal + nonmetal)
(nonmetal + nonmetal)
(metal + polyatomic ion)
Binary Acids
(hydrogen + nonmetal)
1) Name metal
1) Name first element
1) Name metal
2) Use Roman numeral if
2) Use number prefix to show
2) Use Roman numeral if metal
1) All binary acids start with the
metal has variable
number of atoms of first
has variable oxidation number
prefix “hydro”
oxidation number
element (if only one atom, no
3) Name polyatomic ion
2) Name nonmetal
3) Name non-metal
prefix is used)
3) Change ending to -ic
4) Change ending of
3) Name second element
Example: Na
C
O
4) Add the word “acid”
2
2
4
nonmetal to –ide
4) Use number prefix to show
1) Na = sodium
number of atoms of second
2) No Roman numeral needed
Example: HF (aq)
2-
Example: LiF
element
3) C
O
= Oxalate
1) Only 2 elements = binary acid,
2
4
1) Li = lithium
5) Change ending of second
Sodium oxalate
so use the prefix “hydro”
2) Group 1 metal, so no
element to –ide
2) F = fluorine
Roman numeral is
Example: Cu(NO
)
3) Change ending to -ic
3
2
needed
Prefixes:
1=mono
6=hexa
1) Cu = copper
Hydrofluoric acid
3) F = fluorine
2=di
7=hepta
2) Use a Roman numeral to
4) Change ending to -ide
3=tri
8=octa
show charge on metal:
Ternary Acids
2+
1-
Lithium fluoride
4=tetra
9=nona
Cu
(NO
)
Copper(II)
(hydrogen + polyatomic ion)
3
2
1-
5=penta
10=deca
3) NO
= nitrate
3
Example: FeCl
Copper (II) nitrate
1) Skip over the hydrogen(s)
3
1) Fe = iron
Example: N
O
2) Name polyatomic ion
2
5
2) Use a Roman numeral to
1) N = nitrogen
Note for group 7 elements:
3) Change ending:
-
show charge on metal:
2) 2 atoms of nitrogen, so
Per-(_)-ate (ClO
perchlorate)
ate
ic
4
-
3+
1-
iron (III)
use prefix “di”
(_)-ate (ClO
chlorate)
Fe
(Cl
)
ite
ous
3
3
-
3) O = oxygen
(_)-ite
(ClO
chlorite)
3) Cl = chlorine
4) Add the word “acid”
2
-
4) 5 atoms of oxygen, so
Hypo-(_)-ite
(ClO
hypochlorite)
4) Change ending to -ide
-
use prefix “pent(a)”
- ide
(Cl
chloride)
Iron (III) chloride
Example: H
CO
(aq)
2
3
5) Change ending of second
Cl can be replaced with other
1) Skip over the hydrogens
element to -ide
halogens from Group VII
2-
2) CO
= carbonate
3
-
Dinitrogen pentoxide
(F,Br,I) Ex: BrO
perbromate
3) Change –ate to –ic
4
4) Add the word “acid”
Example: CCl
Note: No Roman numeral is
Note: No Roman numeral is
Carbonic acid
4
1) C = carbon
required if the metal is:
required if the metal is:
2) Only one atom of carbon,
Group 1/IA (+1 charge)
Group 1/IA (+1 charge)
Example: HClO (aq)
so no prefix is used
or
or
1) Don’t name hydrogen
3) Cl = chlorine
Group 2/IIA (+2 charge)
1-
Group 2/IIA (+2 charge)
2) ClO
= hypochlorite
4) 4 atoms of chlorine, so use
or
or
3) Change –ite to –ous
3+
2+
2+
1+
3+
2+
2+
1+
prefix “tetra”
Al
Zn
Cd
Ag
Al
Zn
Cd
Ag
4) Add the word “acid”
5) Change ending to –ide
Hypochlorous acid
Carbon tetrachloride
Reprint with permission only: Chandler – Gilbert Community College Learning Center
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1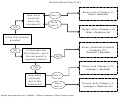 2
2