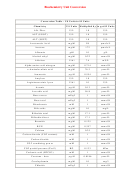
Si - English Unit Conversion Table Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
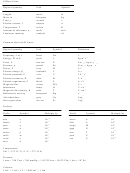
Constants:
Constant Name
Definition
Constant Name
Definition
0 K = −273.15 °C
-15
Absolute zero temperature
Electron radius
r
= 2.81792 × 10
e
8
-1
-1
-1
Speed of light in vacuum
c = 2.99792458 × 10
m·s
Molar gas constant
R = 8.314472 J·mol
·K
−11
3
-1
-2
3
-1
Newtonian constant of gravitation
G = 6.6742 × 10
m
·kg
s
Molar Volume
V
= 22.41383 m
·kmol
mol
−34
-1
h = 6.6260693 × 10
J·Hz
-31
Planck constant
Mass of an electron
m
= 9.1093897 × 10
kg
e
-15
= 4.136 × 10
eV·s;
Planck constant over 2π
-27
−34
Mass of a proton
m
= 1.6726231 × 10
kg
= 1.05457148 × 10
J·s
p
−19
-27
Elementary charge
e = 1.60217653 × 10
C
Mass of a neutron
m
= 1.6749286 × 10
kg
n
−7
μ
2
3
-1
= 4π × 10
T
·m
·J
=
0
23
-1
Avogadro constant
N
= 6.0221415 × 10
mol
Permeability of vacuum
A
−7
2
3
-1
12.566370614 × 10
T
·m
·J
ε
2
= 1/(μ
c
) = 8.854187817 ×
0
0
9
2
-2
Constant in Coulomb's law
K = 8.988 × 10
N·m
·kg
Permittivity of vacuum
−12
2
-1
-1
10
C
·J
·m
α = e
2
/(2ε
hc) = 1/137.0359895 =
0
−23
-1
Boltzmann's constant
k = 1.3806505 × 10
J K
Fine structure constant
-3
7.2974 × 10
−8
−29
σ = 5.670400 × 10
-2
-4
σ
2
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
W·m
·K
Thomson cross-section
= 6.652 × 10
m
e
−27
Unified atomic mass unit
1 u = 1.66056×10
kg
−11
Bohr radius
a
= 5.292 × 10
m
0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
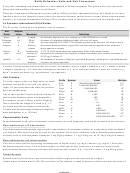
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1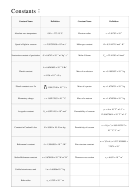 2
2 3
3 4
4