Adult Combined Immunization Schedule Template
ADVERTISEMENT
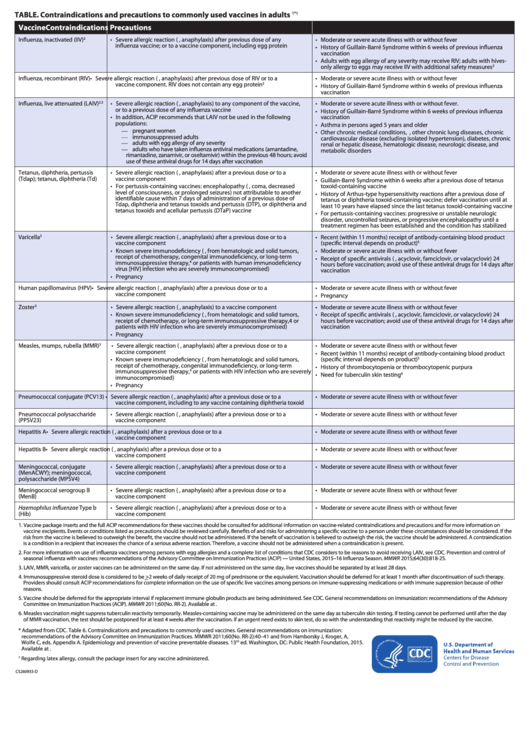
TABLE. Contraindications and precautions to commonly used vaccines in adults
1*†
Vaccine
Contraindications
Precautions
Influenza, inactivated (IIV)
2
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after previous dose of any
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
influenza vaccine; or to a vaccine component, including egg protein
• History of Guillain-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous influenza
vaccination
• Adults with egg allergy of any severity may receive RIV; adults with hives-
only allergy to eggs may receive IIV with additional safety measures
2
Influenza, recombinant (RIV)
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after previous dose of RIV or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component. RIV does not contain any egg protein
2
• History of Guillain-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous influenza
vaccination
Influenza, live attenuated (LAIV)
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to any component of the vaccine,
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
2,3
or to a previous dose of any influenza vaccine
• History of Guillain-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous influenza
• In addition, ACIP recommends that LAIV not be used in the following
vaccination
populations:
• Asthma in persons aged 5 years and older
— pregnant women
• Other chronic medical conditions, e.g., other chronic lung diseases, chronic
— immunosuppressed adults
cardiovascular disease (excluding isolated hypertension), diabetes, chronic
— adults with egg allergy of any severity
renal or hepatic disease, hematologic disease, neurologic disease, and
— adults who have taken influenza antiviral medications (amantadine,
metabolic disorders
rimantadine, zanamivir, or oseltamivir) within the previous 48 hours; avoid
use of these antiviral drugs for 14 days after vaccination
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
(Tdap); tetanus, diphtheria (Td)
vaccine component
• Guillain-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous dose of tetanus
• For pertussis-containing vaccines: encephalopathy (e.g., coma, decreased
toxoid-containing vaccine
level of consciousness, or prolonged seizures) not attributable to another
• History of Arthus-type hypersensitivity reactions after a previous dose of
identifiable cause within 7 days of administration of a previous dose of
tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine; defer vaccination until at
Tdap, diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis (DTP), or diphtheria and
least 10 years have elapsed since the last tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine
tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
• For pertussis-containing vaccines: progressive or unstable neurologic
disorder, uncontrolled seizures, or progressive encephalopathy until a
treatment regimen has been established and the condition has stabilized
Varicella
3
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood product
vaccine component
(specific interval depends on product)
5
• Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic and solid tumors,
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
receipt of chemotherapy, congenital immunodeficiency, or long-term
• Receipt of specific antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24
immunosuppressive therapy,
4
or patients with human immunodeficiency
hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs for 14 days after
virus [HIV] infection who are severely immunocompromised)
vaccination
• Pregnancy
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component
• Pregnancy
Zoster
3
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a vaccine component
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
• Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic and solid tumors,
• Receipt of specific antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24
receipt of chemotherapy, or long-term immunosuppressive therapy,4 or
hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs for 14 days after
patients with HIV infection who are severely immunocompromised)
vaccination
• Pregnancy
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
3
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component
• Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood product
• Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic and solid tumors,
(specific interval depends on product)
5
receipt of chemotherapy, congenital immunodeficiency, or long-term
• History of thrombocytopenia or thrombocytopenic purpura
immunosuppressive therapy,
or patients with HIV infection who are severely
4
• Need for tuberculin skin testing
6
immunocompromised)
• Pregnancy
Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component, including to any vaccine containing diphtheria toxoid
Pneumococcal polysaccharide
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
(PPSV23)
vaccine component
Hepatitis A
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component
Hepatitis B
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
vaccine component
Meningococcal, conjugate
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
(MenACWY); meningococcal,
vaccine component
polysaccharide (MPSV4)
Meningococcal serogroup B
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
(MenB)
vaccine component
Haemophilus influenzae Type b
• Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a
• Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
(Hib)
vaccine component
1. Vaccine package inserts and the full ACIP recommendations for these vaccines should be consulted for additional information on vaccine-related contraindications and precautions and for more information on
vaccine excipients. Events or conditions listed as precautions should be reviewed carefully. Benefits of and risks for administering a specific vaccine to a person under these circumstances should be considered. If the
risk from the vaccine is believed to outweigh the benefit, the vaccine should not be administered. If the benefit of vaccination is believed to outweigh the risk, the vaccine should be administered. A contraindication
is a condition in a recipient that increases the chance of a serious adverse reaction. Therefore, a vaccine should not be administered when a contraindication is present.
2. For more information on use of influenza vaccines among persons with egg allergies and a complete list of conditions that CDC considers to be reasons to avoid receiving LAIV, see CDC. Prevention and control of
seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) — United States, 2015–16 Influenza Season. MMWR 2015;64(30):818-25.
3. LAIV, MMR, varicella, or zoster vaccines can be administered on the same day. If not administered on the same day, live vaccines should be separated by at least 28 days.
4. Immunosuppressive steroid dose is considered to be >2 weeks of daily receipt of 20 mg of prednisone or the equivalent. Vaccination should be deferred for at least 1 month after discontinuation of such therapy.
Providers should consult ACIP recommendations for complete information on the use of specific live vaccines among persons on immune-suppressing medications or with immune suppression because of other
reasons.
5. Vaccine should be deferred for the appropriate interval if replacement immune globulin products are being administered. See CDC. General recommendations on immunization: recommendations of the Advisory
Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR 2011;60(No. RR-2). Available at
6. Measles vaccination might suppress tuberculin reactivity temporarily. Measles-containing vaccine may be administered on the same day as tuberculin skin testing. If testing cannot be performed until after the day
of MMR vaccination, the test should be postponed for at least 4 weeks after the vaccination. If an urgent need exists to skin test, do so with the understanding that reactivity might be reduced by the vaccine.
* Adapted from CDC. Table 6. Contraindications and precautions to commonly used vaccines. General recommendations on immunization:
recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR 2011;60(No. RR-2):40–41 and from Hamborsky J, Kroger, A,
Wolfe C, eds. Appendix A. Epidemiology and prevention of vaccine preventable diseases. 13
th
ed. Washington, DC: Public Health Foundation, 2015.
Available at
Regarding latex allergy, consult the package insert for any vaccine administered.
†
CS260933-D
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1








