Morse Code Chart Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Mohawk Valley Library System
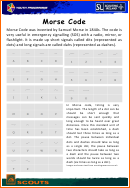
International Morse Code
(Used on land, sea and air to send messages before the Audio Radio)
Telegraph is the sending of information/signals across a distance. Before 1839 telegraphy (the way signals
were sent) used smoke, fire or drum.
In 1830, an American inventor, Joseph Henry (born in Albany, NY), sent an electrical current through a wire
one mile long to energize an electromagnet which caused a bell to sound. Thus the Electric Telegraph was
born.
In 1838 Samuel Morse and his partner Alfred Vail, developed an operator key, which operated a distant
electromagnet. This caused a marker to stamp a series of dots and dashes on a paper roll. The series of
Dots and Dashes represented the letters of the alphabet and numbers, and became known as the Morse
Code.
About 1856 a sounding key was developed that enabled operators to hear the message clicks and write it
directly down in plain language.
Ships used light to send visual messages by flashing the light in Morse Code to anyone they could see. In
1901 the Italian physicist, Guglielmo Marconi, perfected a Radio (wireless) telegraph system to transmitted
messages using Morse Code. Soon after this, Marconi Systems were being installed on ships, then in time,
in all kinds of aircraft. Official use of Morse Code ended in 1999
Try your hand at using Morse Code-
Write your name vertically on a piece of paper. Next to each letter write the dots and dash for that letter.
Make a circuit using the telegraph key and the buzzer. Then tap out your name
J
O
H
N
Sponsored by GE Volunteers: A Global Organization of General Electric Volunteers
and the Mohawk Valley Library System
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1 2
2 3
3