Communicable Disease Chart For Schools And Child-Care Centers
ADVERTISEMENT
Communicable Disease Notes
Communicable Disease Chart for Schools and Child-Care Centers
The major criterion for exclusion from attendance is the probability of spread from person to person. A child may have a noncommunicable illness yet require care at home or in a hospital.
Exclusion and Readmission
Condition
Incubation Period
Signs and Symptoms
Exclusion *
Readmission Criteria
Reportable Disease
Prevention, Treatment and Comments
Children excluded from a school or child-care facility for a communicable disease may be readmitted by a written note from a HCW.
A school or child-care facility administrator may require a note from a parent or HCW for readmission regardless of the reason for the
AIDS/HIV Infection
Variable
Weight loss, generalized swelling of the lymph nodes, failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea,
Yes, but schools are
See AIDS/HIV
When cleaning up spills of blood or body fluids, wear gloves and use a suitable disinfectant.
absence.
tender spleen and liver. Individuals may be asymptomatic.
note below.
not required to report.
Educate adolescents about viral transmission through sexual contact and sharing of equipment
When to Keep Your Child Home from School
for injection.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that your child be kept home from a child-care facility or school if any of the
Amebiasis
Commonly
Intestinal disease may vary from asymptomatic to acute dysentery with bloody diarrhea,
Yes
After treatment is initiated.
Yes, call
Adequate treatment is necessary to prevent or eliminate extraintestinal disease. Teach importance
following conditions exist:
2-4 weeks
fever, and chills. Parasite may disseminate to other internal organs.
(800) 705-8868.
of handwashing. Relatively uncommon in the United States, but can be acquired in developing
Signs of severe illness, including fever, irritability, difficulty breathing, crying that doesn’t stop with the usual comforting, or
●
countries. Spread by personal contact or through food and/or drink.
extreme sleepiness.
Diarrhea or stools that contain blood or mucus.
Campylobacteriosis
Range 1-10 days
Sudden onset of diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, malaise, nausea, and vomiting.
Yes
After diarrhea and fever subside.
Yes, call
Teach importance of handwashing. Frequently a foodborne infection.
●
Commonly 2-5 days
(800) 705-8868.
Vomiting two or more times in 24 hours, unless a physician feels the cause of vomiting is not an infectious disease and the child is
●
in no danger of becoming dehydrated.
Chickenpox (varicella)
Range 2-3 weeks
Fever and rash that may appear first on head, then spread to body. Usually two or three
Yes
Seven days after onset of rash. Immunocompromised indi-
Yes, call
Shingles is a reactivation of the varicella virus. Since contact with the virus may cause chickenpox
Mouth sores and drooling until a physician or the health authority does not feel the condition is infectious.
●
Commonly 13-17 days
crops of new blisters that heal, sometimes leaving scabs.
viduals should not return until all blisters have crusted over.
(800) 705-8868.
in a susceptible child, it is recommended that a case of shingles be treated similar to a case of
Fever or rash or a change in behavior until a physician has determined that the problem is not caused by an infectious disease.
●
chickenpox. Vaccine available.
Common cold
Range 1-5 days
Runny nose, watery eyes, fatigue, coughing, and sneezing.
No,
No
Teach importance of washing hands and covering mouth when coughing or sneezing. Colds are
After fever subsides.
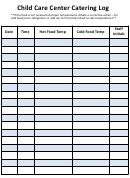
How Some Infectious Diseases Are Spread
Commonly 2 days
unless fever.
caused by viruses; antibiotics are not indicated.
Method of Transmission
Contact
Respiratory Transmission
Fecal-Oral Transmission
Blood
Conjunctivitis, bacterial
Bacterial: 1-3 days
Red eyes, usually with some discharge or crusting around eyes.
Yes
Until effective treatment
No
Teach importance of handwashing. Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and maybe confused
(touching infected
(passing from the lungs, throat,
(touching feces or objects
Transmission
or viral (Pink Eye)
Viral: 12 hours to 12 days
and approval by HCW.
with bacterial and viral conjunctivitis.
person’s skin,
or nose of one person to another
contaminated with feces
(direct contact
body fluid or a
through the air)
then touching your mouth)
with blood)
Coxsackie virus diseases
Commonly 3-5 days
Rash in mouth, hands (palms and fingers), and feet (soles).
No,
No
Promote hand washing and universal precautions.
contaminated surface)
(Hand, Foot & Mouth disease)
unless fever.
Chickenpox *
Chickenpox *
Campylobacter * *
Cytomegalovirus
Cold sores
Common Cold
E. coli 0157:H7 * *
Hepatitis B *
Cryptosporidiosis
Range 1-12 days
Diarrhea, which may be profuse and watery, preceded by anorexia and vomiting in
Yes
After diarrhea subsides.
Yes, call
Teach importance of handwashing.
Conjunctivitis
Diphtheria
Enterovirus
Hepatitis C
Commonly 7 days
children. The diarrhea is associated with abdominal pain. Malaise, fever, nausea, and
(800) 705-8868.
Head Lice
Fifth Disease
Giardia
HIV infection
vomiting occur less often. Infection may be asymptomatic.
Impetigo
Bacterial Meningitis *
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease
Ringworm
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease
Hepatitis A *
Cytomegalovirus
Unknown under normal
Usually asymptomatic. Congenital CMV infections may result in hearing loss,
No
No
Teach importance of good handwashing. Avoid direct contact with urine, saliva, or other infectious
Scabies
Impetigo
Infectious Diarrhea
(CMV) infection
circumstances
pneumonia, eye inflammation, and growth and/or mental retardation.
secretions.
Influenza *
Measles *
Pinworms
Hepatitis B *
Mumps *
Polio *
Pertussis *
Rubella *
Salmonella * *
Escherichia coli
10 hours to 8 days in most
Profuse, watery diarrhea, sometimes with blood and/or mucus, and abdominal pain. Fever
Yes
After diarrhea and fever subside.
Yes, if E. coli 0157:H7 strain.
Teach importance of handwashing. Usually a foodborne infection. Also spread by hand to mouth
Pneumonia
Influenza*
Shigella
(E. coli) infection
cases; for E. coli 0157:H7,
and vomiting may occur. Some strains (such as E. coli 0157:H7) may cause hemolytic
Call (800) 705-8868
contact.
Cryptosporidiosis
commonly 3-4 days
uremic syndrome, resulting in kidney damage.
* Vaccines are available for preventing these diseases
Fever
Oral temperature of 38ºC (100.4ºF) or greater. Measure when no antipyretics are given.
Yes
After fever subsides.
No
Children should not be given aspirin for symptoms of any viral disease, confirmed or suspected,
* * Often transmitted from infected animals through foods or direct contact
without consulting a physician.
Nuisance Diseases
Fifth Disease
Variable: 4-20 days
Redness of the cheeks and body. Rash may reappear. Fever does not usually occur.
No,
After fever subsides.
No
Individual should be seen by a physician to rule out a diagnosis of measles or rubella. Pregnant
So-called “nuisance” diseases, such as scabies, head lice (pediculosis), ringworm of the body or scalp, and pinworms are highly
Human Parvovirus
unless fever.
women who have been exposed should consult their physician.
contagious and can cause problems in a group-care setting. Children and adults with these conditions (except ringworm of the body
and pinworms) should be excluded until treated. Family members, as well as adult caregivers and their families, should be aware of
Gastroenteritis, viral
Variable, usually 1-3 days
Nausea and diarrhea. Fever does not usually occur.
Yes
After diarrhea subsides.
No
Teach importance of good handwashing.
symptoms and treated if they become infected.
Giardiasis
Range 3-25 days or longer
Gradual onset of nausea, bloating, pain, and foul-smelling diarrhea. May recur several
Yes
After diarrhea subsides.
No
Treatment is recommended. Teach importance of good handwashing. Can spread quickly in
Vaccine Preventable Diseases
Commonly 7-10 days
times over a period of weeks.
child-care facilities. Check household contacts for evidence of infection.
Many diseases are preventable by vaccination. Child-care facilities and schools are required to have an immunization record on file for
each child enrolled to ensure that each child has received age-appropriate immunizations. Required vaccines include: DTaP (diphthe-
Head lice
Eggs hatch in 7-10 days
Itching and scratching of scalp. Presence of pinpoint-sized white eggs (nits) that will
Yes, with
After one medicated shampoo or lotion treatment has
No
Second shampoo or lotion treatment is recommended in 7 – 10 days. Teach importance of not
ria, tetanus and pertussis); Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b); polio; MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella); hepatitis B; chickenpox
(Pediculosis)
not flick off the hair shaft and live lice.
live lice.
been given.
sharing combs, brushes, hats, and coats. Check household contacts for evidence of infestation.
(varicella) and hepatitis A in some areas. Vaccines are also available for flu (influenza) and pneumococcal disease. For immunization
information, contact your local health department or call (800) 252-9152.
Yes, call
Hepatitis A
Range 15-50 days
Most children have no symptoms; some have flu-like symptoms or diarrhea. Adults
Yes
One week after onset of illness.
Vaccine available. Teach importance of handwashing. Immune globulin should be given to
Commonly 25-30 days
may have fatigue, nausea and vomiting, anorexia, and abdominal pain. Jaundice, dark
(800) 705-8868.
household contacts. If more than one case occurs in a child-care facility, immune globulin should
Diarrheal Disease
urine, or diarrhea may or may not be present.
be considered for all contacts at the facility.
Many different viral and bacterial agents may cause diarrhea. Exclude until diarrhea has resolved or until cleared by child’s physician
or health department. Antibiotic treatment may be recommended in some cases when outbreaks occur.
Hepatitis B
Range 1
1
/
-6 months
Gradual onset of fever, fatigue, nausea, or vomiting, followed by jaundice. Frequently
No
Yes, call
Vaccine available. Teach importance of handwashing and not sharing razors or toothbrushes. Wear
2
Commonly 2-3 months
asymptomatic in children.
(800) 705-8868.
gloves and use a suitable disinfectant when cleaning up spills of blood or body fluids. Educate
To Minimize the Spread of Communicable Disease
adolescents about viral transmission through sexual contact and sharing of equipment for injection.
Encourage children and adults to wash their hands frequently, especially before handling or preparing foods and after wiping
●
noses, diapering, or using toilets. Sinks, soap, and disposable towels should be easy for children to use. The diapering area
Herpes Simplex
First infection,
Blisters on or near lips that open and become covered with a dark crust. Recurrences
No
No
Teach importance of good hygiene. Avoid direct contact with sores. Antivirals are sometimes
should be close to a handwashing area.
(cold sores)
2-17 days
are common.
used.
Provide facial tissue throughout the facility and encourage both children and adults to cough or sneeze into the tissue.
●
Impetigo
Variable, usually
Blisters on skin, commonly hands and face, that open and become covered with
Yes
After treatment has begun.
No
Keep lesions covered. Teach importance of handwashing and keeping fingernails clean.
Regularly clean and sanitize all food service utensils, toys, and other items used by children. Discourage the use of stuffed toys
●
4-10 days
yellowish crust. Fever does not usually occur.
or other toys that cannot be sanitized.
Diapering and food preparation areas should be physically separate from one another and their surfaces should be kept clean,
●
Influenza (flu)
Commonly 1-3 days
Rapid onset of fever, headache, sore throat, dry cough, chills, lack of energy, and
Yes
After fever subsides.
No
Vaccine available and recommended for children age 6-24 months and those with certain chronic
uncluttered, and dry.
muscle aches.
diseases. Anti-viral therapy available for patients with influenza types A and B.
Discourage children and adults from sharing items such as combs, brushes, jackets, hats, and bedding. Maintain a separate
●
container to store clothing and other personal items and, if possible, provide a separate sleeping area for each child.
Measles (rubeola)
Range 7-18 days
Runny nose, watery eyes, fever, and dry cough. A blotchy red rash, which usually
Yes
Four days after onset of rash.
Yes, immediately call
Vaccine available. In an outbreak, unimmunized children should be excluded for at least two
Wash bedding frequently. Keep changes of clothing on hand and store soiled items in a non-absorbent container that can be
Commonly 8-12 days
begins on the face, appears between the third and seventh day.
(800) 705-8868.
weeks after last rash onset.
●
sanitized or discarded after use.
Meningitis, bacterial
Commonly 2-10 days
Sudden onset of high fever and headache, usually with vomiting.
Yes
Until effective treatment
Yes, call
Prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended for family members and close contacts at a child-
Keep in mind that having staff members diaper children and prepare food contributes to the spread of illness, especially
●
and approval by HCW.
(800) 705-8868.
care facility. Vaccine available for Haemophilus influenzae type B and pneumococcal disease.
diarrheal illnesses. Therefore, whenever possible, the same staff member should not perform both tasks.
When a Communicable Disease is Diagnosed or Suspected
Meningitis, viral
Commonly 2-10 days
Sudden onset of fever and headache, usually with vomiting.
No, unless fever.
When fever subsides.
Yes, call (800) 705-8868.
Teach importance of handwashing.
Segregate the ill child from well children at the facility until he/she can be taken home.
●
Meningococcal infections
Range 2-10 days
Sudden onset of fever, intense headache, nausea and often vomiting, stiff neck, and,
Yes
Until effective treatment
Yes, immediately call
Prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended for family members and close contacts at a child-
Adhere to the exclusion and readmission recommendations provided on the chart.
●
(meningitis, meningococcemia)
Commonly 3-4 days
frequently, a reddish or purplish rash on the skin or mucous membranes.
and approval by HCW.
(800) 705-8868.
care facility. In an outbreak, vaccine may be recommended for persons likely to have been exposed.
Children or adults with fever should not be readmitted until fever subsides.
■
Children or adults with diarrhea should not be readmitted until diarrhea subsides.
Mononucleosis, infectious
Commonly 30-50 days
Variable. Infants and young children are generally asymptomatic. Symptoms, when
Yes
When a physician decides or after fever subsides. Some
No
Minimize contact with saliva or nasal discharges. Teach importance of handwashing. Sanitize
■
Children or adults with conjunctivitis, bacterial meningitis, or tuberculosis should not be readmitted without a note from
■
(Epstein Barr virus)
present, include fever, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and sore throat.
children with fatigue may not be physically able to return to
surfaces and shared items.
their HCW.
school until symptoms subside.
Inform all parents of exposed children about the illness. Ask parents to watch their children for signs and symptoms of the
●
disease.
Mumps
Range 12-25 days
Swelling over jaw in front of one or both ears. Pain in cheeks made worse by chewing.
Yes, call
Yes
After nine days from the onset of swelling.
Vaccine available.
Commonly 16-18 days
(800) 705-8868.
Observe the appearance and behavior of exposed children and be alert to the onset of disease. Let parents know immediately
●
so that medical advice and treatment can be sought.
Otitis media (earache)
Variable
Fever, ear pain. May follow respiratory illness.
No, unless fever.
After fever subsides.
No
Antibiotics are only indicated for acute otitis media.
Utilize a sanitizing procedure (see below) and encourage staff and children to take extra precautions with handwashing,
●
foodhandling, dishwashing, and general cleanliness. Immediately wash, rinse, and sanitize any object or surface that has been
Pertussis
Range 6-21 days
Low-grade fever, runny nose, and cough lasting about two weeks, followed by
Yes
Yes, immediately call
After completion of five days of antibiotic therapy.
Vaccine available. Unimmunized contacts should be immunized and receive antibiotic prophy-
soiled with discharge (such as nasal discharge or feces). Sanitize diaper-changing tables, toilets, and potty chairs after each
(whooping cough)
Commonly 7-10 days
paroxysmal coughing spells and “whoop” on inspiration.
(800) 705-8868.
laxis. Adults with persistent cough greater than 2 weeks should be evaluated.
use.
Pharyngitis, nonstreptococcal
Variable
Fever, sore throat, often with large, tender lymph nodes in neck.
No,
After fever subsides.
No
Nonstreptococcal pharyngitis is caused by a virus; antibiotics are not indicated.
Sanitizing Procedure
(sore throat)
unless fever.
Each day, sanitize all toys and play equipment that are handled or mouthed by children, as follows:
Wash the surface with soap and water.
●
Pinworms
Variable, 2 weeks-
Perianal itching.
No
No
Treatment recommended. Teach importance of handwashing. Check household contact for
Submerge in a fresh solution of 1/4 cup of household bleach per gallon of water or an approved product (spray or wipe those
2 months or longer
infestations.
●
items which cannot be submerged).
Ringworm of the body
Commonly 4-10 days
Slowly spreading, flat, scaly, ring-shaped lesions on skin. Margins may be reddish & slightly
No
No
Treatment is recommended. Keep lesions covered. A fungal infection.
Rinse in clean water and air dry.
●
raised.
Diapering
Ringworm of the scalp
Commonly 10-21 days
Slowly spreading, round, scaly balding patches on scalp with broken-off hairs.
Yes
After treatment has begun.
No
Teach importance of not sharing combs, brushes, hats, and coats. A fungal infection.
The diapering surface should have a plastic-covered pad with no cracks or tears. If the diapering surface cannot be easily
●
cleaned after each use, then use a disposable material such as a paper sheet, shelf paper, wax paper, scrap computer paper, or
Rubella
Range 14-23 days
Cold-like symptoms. Swollen, tender glands at the back of the neck. Fever. Change-
Yes
Seven days after onset of rash.
Yes, call (800) 705-8868
Vaccine available. In an outbreak, unimmunized children and pregnant women should be ex-
paper base on the changing table; discard after each diapering.
(German measles)
Commonly 16-18 days
able pink rash on face and chest.
within one working day.
cluded for at least three weeks after last rash onset.
Sanitize the diapering surface after each use and at the end of each day.
●
Salmonellosis
Range 6-72 hours
Yes, call (800) 705-8868.
Wash hands with soap and warm water immediately after diapering each child. Be careful to clean under the fingernails.
Sudden onset of fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and sometimes vomiting.
Yes
After diarrhea and fever subside.
Teach importance of handwashing. Frequently a foodborne infection.
●
Commonly 12-36 hours
Antibiotic Use
Scabies
First infection: 2-6 weeks
Small, raised and red bumps or blisters on skin with severe itching. Often the thighs,
Yes
After treatment has begun.
No
Teach importance of not sharing clothing. May have rash and itching after treatment, but will
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections. Since most common colds, coughs, runny noses, and sore throats are caused by
viruses, not bacteria, treatment with antibiotics is not indicated. Unnecessary antibiotic use can lead to the development of drug-
Repeat infection: 1-4 days
arms, and webs of fingers.
subside.
resistant strains of bacteria. Diseases caused by resistant bacteria are often difficult to treat and can be especially severe and prolonged.
Sinus infection
Variable
Fever, headache, greenish to yellowish mucus for more than one week.
No
No
Antibiotics are only indicated for long-lasting or severe sinus infections.
Wound Care
Shigellosis
Range 1-7 days
Sudden onset of fever, vomiting, and diarrhea, which may be bloody.
Yes
After diarrhea and fever subside.
Yes, call (800) 705-8868.
Teach importance of handwashing. Can spread quickly in child-care facilities.
Manage any draining wound as a potential antibiotic-resistant infection. Do not allow staff and children with a draining wound (infec-
Commonly 2-3 days
tion) to have physical contact with others until the wound has stopped draining and has healed. Separate other children from the
infected child’s wound or a contaminated physical environment. Keep the wound covered. Do not share soap, towels, lotions, and other
personal care items. Disinfect reusable items such as desks, chairs, pencils, and scissors. Use proper procedures for disposal of con-
Streptococcal sore throat
Commonly 1-3 days
Fever, sore throat, often with large, tender lymph nodes in neck. Scarlet fever-producing
Yes
Twenty-four hours after effective antibiotic treatment
No
Teach importance of covering mouth when coughing or sneezing. Streptococcal sore throat can
taminated items. Encourage parents to take the child to a physician for a culture and susceptibility test of the drainage. Contact the
and scarlet fever
strains of bacteria cause a fine, red rash that appears 1-3 days after onset of sore throat.
has begun and fever subsides.
only be diagnosed with a laboratory test.
Infectious Disease Control Unit for Staphylococcus aureus Guidelines in Child Care Setting: School or Day Care.
Tuberculosis, pulmonary
Commonly 2-12 weeks
Gradual onset, fatigue, anorexia, fever, failure to gain weight, and cough.
Yes
After antibiotic treatment has begun AND a
Yes, call (800) 705-8868
All classroom contacts should have TB skin tests. Antibiotic prophylaxis recommended for newly
HCW — health care worker (physician, local health authority, advance practice nurse, physician’s assistant)
within one working day.
positive reactors. Call the TB control program at your local health department for contact testing.
physician’s certificate or health permit obtained.
*For conditions specified in the Texas Administrative Code. ■
Infectious Disease Information — (512-458-7676) – ■
Immunization Information — (800-252-9152) – ■ HCW — health care worker (physician, local health authority, advance practice nurse, physician’s assistant)
Stock No. 6-30 (8/2004)
AIDS/HIV
: Not excluded unless child’s physician determines that a severe or chronic skin eruption or lesion that cannot be covered poses a threat to others. The child’s parents and physician should be advised in the case of measles, rubella, or chickenpox outbreaks in school. These may pose a health threat to the immunosuppressed child.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1