Additional Science - Chemistry Checklist
ADVERTISEMENT
A
S
C3: C
DDITIONAL
CIENCE
HEMISTRY
!
Higher content bold & labeled as HT
"
Key words in bold
#
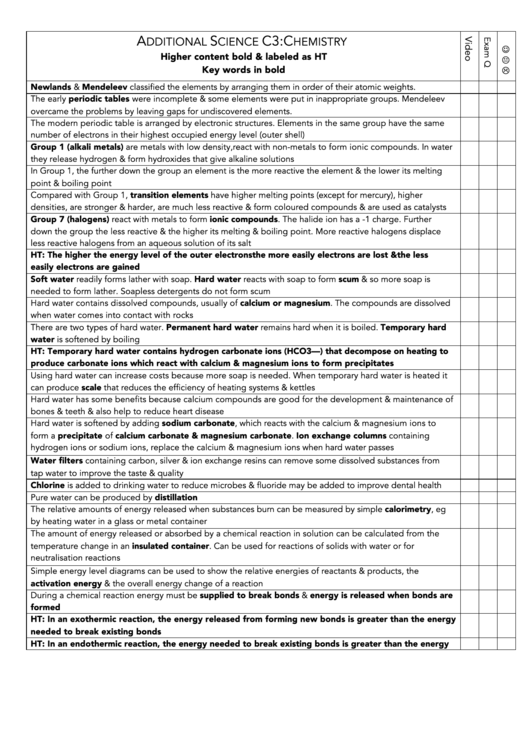
Newlands & Mendeleev classified the elements by arranging them in order of their atomic weights.
The early periodic tables were incomplete & some elements were put in inappropriate groups. Mendeleev
overcame the problems by leaving gaps for undiscovered elements.
The modern periodic table is arranged by electronic structures. Elements in the same group have the same
number of electrons in their highest occupied energy level (outer shell)
Group 1 (alkali metals) are metals with low density, react with non-metals to form ionic compounds. In water
they release hydrogen & form hydroxides that give alkaline solutions
In Group 1, the further down the group an element is the more reactive the element & the lower its melting
point & boiling point
Compared with Group 1, transition elements have higher melting points (except for mercury), higher
densities, are stronger & harder, are much less reactive & form coloured compounds & are used as catalysts
Group 7 (halogens) react with metals to form ionic compounds. The halide ion has a -1 charge. Further
down the group the less reactive & the higher its melting & boiling point. More reactive halogens displace
less reactive halogens from an aqueous solution of its salt
HT: The higher the energy level of the outer electrons the more easily electrons are lost & the less
easily electrons are gained
Soft water readily forms lather with soap. Hard water reacts with soap to form scum & so more soap is
needed to form lather. Soapless detergents do not form scum
Hard water contains dissolved compounds, usually of calcium or magnesium. The compounds are dissolved
when water comes into contact with rocks
There are two types of hard water. Permanent hard water remains hard when it is boiled. Temporary hard
water is softened by boiling
HT: Temporary hard water contains hydrogen carbonate ions (HCO3––) that decompose on heating to
produce carbonate ions which react with calcium & magnesium ions to form precipitates
Using hard water can increase costs because more soap is needed. When temporary hard water is heated it
can produce scale that reduces the efficiency of heating systems & kettles
Hard water has some benefits because calcium compounds are good for the development & maintenance of
bones & teeth & also help to reduce heart disease
Hard water is softened by adding sodium carbonate, which reacts with the calcium & magnesium ions to
form a precipitate of calcium carbonate & magnesium carbonate. Ion exchange columns containing
hydrogen ions or sodium ions, replace the calcium & magnesium ions when hard water passes
Water filters containing carbon, silver & ion exchange resins can remove some dissolved substances from
tap water to improve the taste & quality
Chlorine is added to drinking water to reduce microbes & fluoride may be added to improve dental health
Pure water can be produced by distillation
The relative amounts of energy released when substances burn can be measured by simple calorimetry, eg
by heating water in a glass or metal container
The amount of energy released or absorbed by a chemical reaction in solution can be calculated from the
temperature change in an insulated container. Can be used for reactions of solids with water or for
neutralisation reactions
Simple energy level diagrams can be used to show the relative energies of reactants & products, the
activation energy & the overall energy change of a reaction
During a chemical reaction energy must be supplied to break bonds & energy is released when bonds are
formed
HT: In an exothermic reaction, the energy released from forming new bonds is greater than the energy
needed to break existing bonds
HT: In an endothermic reaction, the energy needed to break existing bonds is greater than the energy
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2