Nucleophilicity, Basicity And Leaving Group Ability
ADVERTISEMENT
CHM 331/332 handout (page 1 of 3)
NUCLEOPHILICITY, BASICITY AND LEAVING GROUP ABILITY
____________________________________________________________
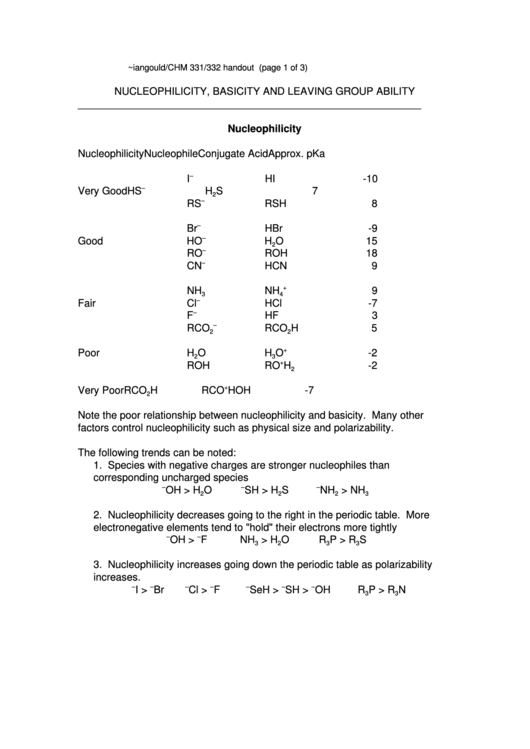
Nucleophilicity
Nucleophilicity
Nucleophile
Conjugate Acid
Approx. pKa
–
I
HI
-10
–
Very Good
HS
H
S
7
2
–
RS
RSH
8
–
Br
HBr
-9
–
Good
HO
H
O
15
2
–
RO
ROH
18
–
CN
HCN
9
+
NH
NH
9
3
4
–
Fair
Cl
HCl
-7
–
F
HF
3
–
RCO
RCO
H
5
2
2
+
Poor
H
O
H
O
-2
2
3
+
ROH
RO
H
-2
2
+
Very Poor
RCO
H
RCO
HOH
-7
2
Note the poor relationship between nucleophilicity and basicity. Many other
factors control nucleophilicity such as physical size and polarizability.
The following trends can be noted:
1. Species with negative charges are stronger nucleophiles than
corresponding uncharged species
–
–
–
OH > H
O
SH > H
S
NH
> NH
2
2
2
3
2. Nucleophilicity decreases going to the right in the periodic table. More
electronegative elements tend to "hold" their electrons more tightly
–
–
OH >
F
NH
> H
O
R
P > R
S
3
2
3
3
3. Nucleophilicity increases going down the periodic table as polarizability
increases.
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
I >
Br
Cl >
F
SeH >
SH >
OH
R
P > R
N
3
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3