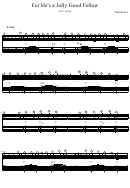
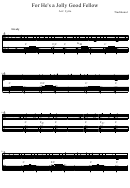
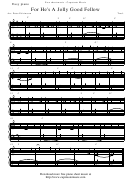
Formula Card For Weiss'S Elementary Statistics, Fourth Edition
ADVERTISEMENT
FORMULA CARD FOR WEISS’S ELEMENTARY STATISTICS, FOURTH EDITION
Larry R. Griffey
•
NOTATION In the formulas below, unless stated otherwise, we
Linear correlation coefficient:
(x
x)(y
y)
employ the following notation which may or may not appear with
1
S
xy
n 1
r
r
or
subscripts:
s
s
S
S
x
y
xx
yy
n
σ
sample size
population stdev
x
d
sample mean
paired difference
CHAPTER 5
Probability and Random Variables
s
ˆ p
sample stdev
sample proportion
•
Probability for equally likely outcomes:
Q
j th quartile
p
population proportion
j
f
P (E)
,
N
O
population size
observed frequency
N
µ
E
population mean
expected frequency
where f denotes the number of ways event E can occur and
N denotes the total number of outcomes possible.
CHAPTER 3
Descriptive Measures
•
Special addition rule:
x
P (A or B or C or · · · )
P (A) + P (B) + P (C) + · · ·
•
Sample mean: x
n
(A, B, C, . . . mutually exclusive)
•
Range: Range
Max
Min
•
Complementation rule: P (E)
P (not E)
1
•
Sample standard deviation:
•
General addition rule: P (A or B)
P (A) + P (B)
P (A & B)
(x
x)
x
( x)
/n
2
2
2
s
s
or
•
Mean of a discrete random variable X: µ
xP (X
x)
n
n
1
1
•
Standard deviation of a discrete random variable X:
•
Quartile positions: (n + 1)/4, (n + 1)/2, 3(n + 1)/4
σ
(x
µ)
P (X
x)
σ
x
P (X
x)
µ
2
2
2
or
•
Q
Q
Interquartile range: IQR
3
1
•
Factorial: k!
k(k
1) · · · 2 · 1
•
Q
1.5 · IQR,
Q
+ 1.5 · IQR
Lower limit
Upper limit
1
3
n
n!
x
•
Binomial coefficient:
•
Population mean (mean of a variable): µ
x
x! (n
x)!
N
•
•
Binomial probability formula:
Population standard deviation (standard deviation of a variable):
n
x
n x
P (X
x)
p
(1
p)
,
(x
µ)
x
2
2
x
σ
σ
µ
2
or
N
N
where n denotes the number of trials and p denotes the success
x
µ
probability.
•
Standardized variable: z
σ
•
Mean of a binomial random variable: µ
np
CHAPTER 4
Descriptive Methods in Regression and Correlation
•
Standard deviation of a binomial random
variable: σ
np(1
p)
•
S
, S
, and S
:
xx
xy
yy
S
(x
x)
2
x
2
( x)
2
/n
xx
CHAPTER 7
The Sampling Distribution of the Mean
S
(x
x)(y
y)
xy
( x)( y)/n
xy
•
Mean of the variable x: µ
µ
x
S
(y
y)
y
( y)
/n
2
2
2
√
yy
•
Standard deviation of the variable x: σ
σ/
n
x
•
Regression equation: ˆ y
b
+ b
x, where
0
1
•
Standardized version of the variable x:
S
1
xy
b
b
( y
b
x)
y
b
x
x
µ
and
1
0
1
1
S
n
z
√
xx
σ/
n
•
(y
y)
2
S
Total sum of squares: SST
yy
CHAPTER 8
Confidence Intervals for One Population Mean
•
( ˆ y
y)
2
S
2
/S
Regression sum of squares: SSR
xx
xy
•
z-interval for µ (σ known, normal population or large sample):
•
(y
ˆ y)
2
S
S
2
/S
Error sum of squares: SSE
yy
xx
xy
σ
x ± z
·
√
α/2
•
SSR + SSE
n
Regression identity: SST
σ
SSR
•
Margin of error for the estimate of µ: E
z
·
√
•
Coefficient of determination: r
2
α/2
n
SST
-1-
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3