Factoring Cheat Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Factoring Cheat Sheet
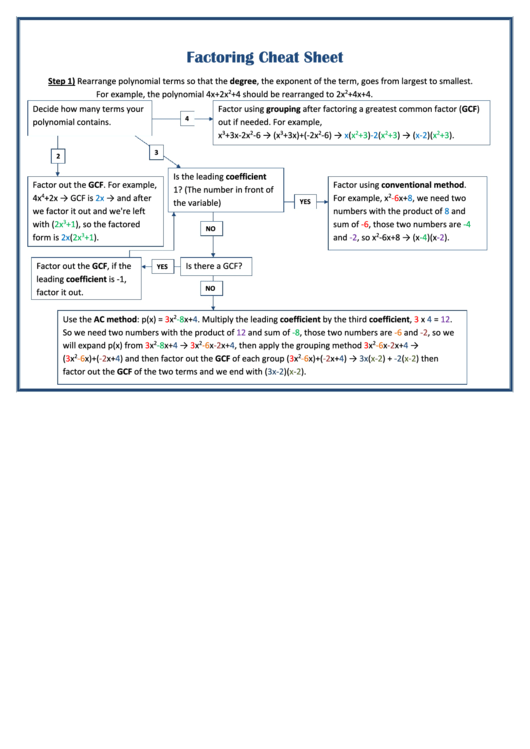
Step 1) Rearrange polynomial terms so that the degree, the exponent of the term, goes from largest to smallest.
2
2
For example, the polynomial 4x+2x
+4 should be rearranged to 2x
+4x+4.
Decide how many terms your
Factor using grouping after factoring a greatest common factor (GCF)
4
polynomial contains.
out if needed. For example,
3
2
3
2
2
2
2
x
+3x‐2x
‐6 → (x
+3x)+(‐2x
‐6) → x(x
+3)‐2(x
+3) → (x‐2)(x
+3).
3
2
Is the leading coefficient
Factor out the GCF. For example,
Factor using conventional method.
1? (The number in front of
4
2
4x
+2x → GCF is 2x → and a er
For example, x
‐6x+8, we need two
the variable)
YES
we factor it out and we're left
numbers with the product of 8 and
3
with (2x
+1), so the factored
sum of ‐6, those two numbers are ‐4
NO
3
2
form is 2x(2x
+1).
and ‐2, so x
‐6x+8 → (x‐4)(x‐2).
Factor out the GCF, if the
Is there a GCF?
YES
leading coefficient is ‐1,
NO
factor it out.
2
Use the AC method: p(x) = 3x
‐8x+4. Multiply the leading coefficient by the third coefficient, 3
x 4
= 12.
So we need two numbers with the product of 12 and sum of ‐8, those two numbers are ‐6 and ‐2, so we
2
2
2
will expand p(x) from 3x
‐8x+4 → 3x
‐6x‐2x+4, then apply the grouping method 3x
‐6x‐2x+4 →
2
2
(3x
‐6x)+(‐2x+4) and then factor out the GCF of each group (3x
‐6x)+(‐2x+4) → 3x(x‐2) + ‐2(x‐2) then
factor out the GCF of the two terms and we end with (3x‐2)(x‐2).
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1