A Matlab Cheat-Sheet (Mit 18.06, Fall 2007)
ADVERTISEMENT
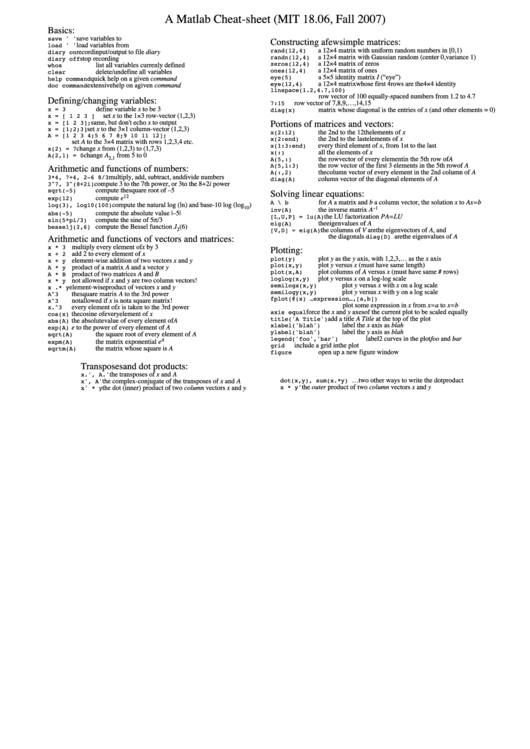
A Matlab Cheat-sheet (MIT 18.06, Fall 2007)
Basics:
save variables to file.mat
save 'file.mat'
Constructing a few simple matrices:
load variables from file.mat
load 'file.mat'
a 12×4 matrix with uniform random numbers in [0,1)
rand(12,4)
record input/output to file diary
diary on
a 12×4 matrix with Gaussian random (center 0, variance 1)
randn(12,4)
stop recording
diary off
a 12×4 matrix of zeros
zeros(12,4)
list all variables currenly defined
whos
a 12×4 matrix of ones
ones(12,4)
delete/undefine all variables
clear
a 5×5 identity matrix I (“eye”)
eye(5)
quick help on a given command
help command
a 12×4 matrix whose first 4 rows are the 4×4 identity
eye(12,4)
extensive help on a given command
doc command
linspace(1.2,4.7,100)
row vector of 100 equally-spaced numbers from 1.2 to 4.7
Defining/changing variables:
row vector of 7,8,9,…,14,15
7:15
define variable x to be 3
x = 3
matrix whose diagonal is the entries of x (and other elements = 0)
diag(x)
set x to the 1×3 row-vector (1,2,3)
x = [1 2 3]
same, but don't echo x to output
x = [1 2 3];
Portions of matrices and vectors:
set x to the 3×1 column-vector (1,2,3)
x = [1;2;3]
the 2nd to the 12th elements of x
x(2:12)
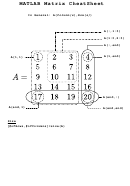
A = [1 2 3 4;5 6 7 8;9 10 11 12];
the 2nd to the last elements of x
x(2:end)
set A to the 3×4 matrix with rows 1,2,3,4 etc.
every third element of x, from 1st to the last
x(1:3:end)
change x from (1,2,3) to (1,7,3)
x(2) = 7
all the elements of x
x(:)
change A
from 5 to 0
A(2,1) = 0
2,1
the row vector of every element in the 5th row of A
A(5,:)
the row vector of the first 3 elements in the 5th row of A
A(5,1:3)
Arithmetic and functions of numbers:
the column vector of every element in the 2nd column of A
A(:,2)
multiply, add, subtract, and divide numbers
3*4, 7+4, 2-6 8/3
column vector of the diagonal elements of A
diag(A)
compute 3 to the 7th power, or 3 to the 8+2i power
3^7, 3^(8+2i)
compute the square root of –5
sqrt(-5)
Solving linear equations:
12
compute e
exp(12)
for A a matrix and b a column vector, the solution x to Ax=b
A \ b
compute the natural log (ln) and base-10 log (log
)
log(3), log10(100)
10
–1
the inverse matrix A
inv(A)
compute the absolute value |–5|
abs(-5)
the LU factorization PA=LU
[L,U,P] = lu(A)
compute the sine of 5π/3
sin(5*pi/3)
the eigenvalues of A
eig(A)
compute the Bessel function J
(6)
besselj(2,6)
the columns of V are the eigenvectors of A, and
2
[V,D] = eig(A)
the diagonals
are the eigenvalues of A
diag(D)
Arithmetic and functions of vectors and matrices:
multiply every element of x by 3
x * 3
Plotting:
add 2 to every element of x
x + 2
plot y as the y axis, with 1,2,3,… as the x axis
plot(y)
element-wise addition of two vectors x and y
x + y
plot y versus x (must have same length)
plot(x,y)
product of a matrix A and a vector y
A * y
plot columns of A versus x (must have same # rows)
plot(x,A)
product of two matrices A and B
A * B
plot y versus x on a log-log scale
loglog(x,y)
not allowed if x and y are two column vectors!
x * y
plot y versus x with x on a log scale
semilogx(x,y)
element-wise product of vectors x and y
x .* y
plot y versus x with y on a log scale
semilogy(x,y)
the square matrix A to the 3rd power
A^3
fplot(@(x) …expression…,[a,b])
not allowed if x is not a square matrix!
x^3
plot some expression in x from x=a to x=b
every element of x is taken to the 3rd power
x.^3
force the x and y axes of the current plot to be scaled equally
axis equal
the cosine of every element of x
cos(x)
add a title A Title at the top of the plot
title('A Title')
the absolute value of every element of A
abs(A)
label the x axis as blah
xlabel('blah')
e to the power of every element of A
exp(A)
label the y axis as blah
ylabel('blah')
the square root of every element of A
sqrt(A)
label 2 curves in the plot foo and bar
legend('foo','bar')
A
the matrix exponential e
expm(A)
include a grid in the plot
grid
the matrix whose square is A
sqrtm(A)
open up a new figure window
figure
Transposes and dot products:
the transposes of x and A
x.', A.'
…two other ways to write the dot product
dot(x,y), sum(x.*y)
the complex-conjugate of the transposes of x and A
x', A'
the outer product of two column vectors x and y
the dot (inner) product of two column vectors x and y
x * y'
x' * y
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1