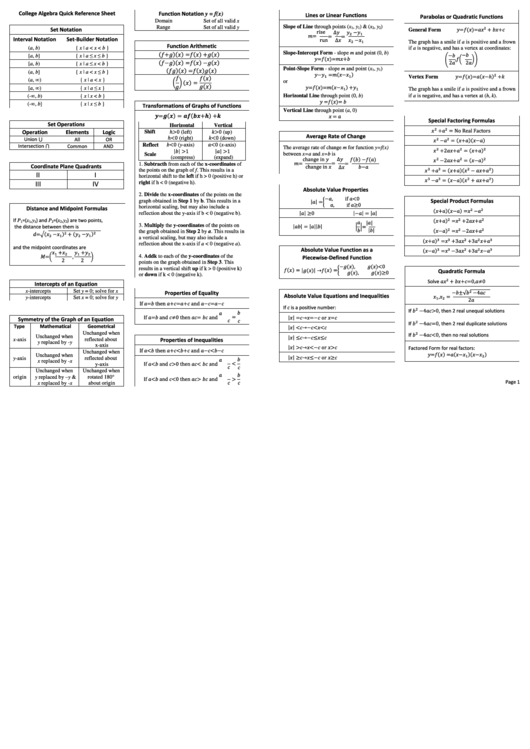
College Algebra Quick Reference Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
College Algebra Quick Reference Sheet
Function Notation y = f(x)
Lines or Linear Functions
Parabolas or Quadratic Functions
Domain
Set of all valid x
Slope of Line through points (x
, y
) & (x
, y
)
Range
Set of all valid y
Set Notation
1
1
2
2
General Form
Interval Notation
Set-Builder Notation
The graph has a smile if a is positive and a frown
Function Arithmetic
(a, b)
{ x | a < x < b }
if a is negative, and has a vertex at coordinates:
Slope-Intercept Form - slope m and point (0, b)
{ x | a ≤ x ≤ b }
[a, b]
{ x | a ≤ x < b }
[a, b)
Point-Slope Form - slope m and point (x
, y
)
{ x | a < x ≤ b }
1
1
(a, b]
Vertex Form
(a, ∞)
{ x | a < x }
or
[a, ∞)
{ x | a ≤ x }
The graph has a smile if a is positive and a frown
(-∞, b)
{ x | x < b }
Horizontal Line through point (0, b)
if a is negative, and has a vertex at (h, k).
{ x | x ≤ b }
(-∞, b]
Transformations of Graphs of Functions
Vertical Line through point (a, 0)
Special Factoring Formulas
Set Operations
Horizontal
Vertical
Operation
Elements
Logic
Shift
(left)
(up)
Average Rate of Change
(right)
(down)
Union
All
OR
Reflect
(y-axis)
(x-axis)
Intersection
Common
AND
The average rate of change m for function y=f(x)
between x=a and x=b is
Scale
(compress)
(expand)
1. Subtract h from each of the x-coordinates of
Coordinate Plane Quadrants
the points on the graph of f. This results in a
II
I
horizontal shift to the left if h > 0 (positive h) or
right if h < 0 (negative h).
III
IV
Absolute Value Properties
2. Divide the x-coordinates of the points on the
Special Product Formulas
graph obtained in Step 1 by b. This results in a
horizontal scaling, but may also include a
Distance and Midpoint Formulas
reflection about the y-axis if b < 0 (negative b).
If P
=(x
,y
) and P
=(x
,y
) are two points,
1
1
1
2
2
2
3. Multiply the y-coordinates of the points on
the distance between them is
the graph obtained in Step 2 by a. This results in
a vertical scaling, but may also include a
reflection about the x-axis if a < 0 (negative a).
and the midpoint coordinates are
Absolute Value Function as a
4. Add k to each of the y-coordinates of the
Piecewise-Defined Function
points on the graph obtained in Step 3. This
results in a vertical shift up if k > 0 (positive k)
Quadratic Formula
or down if k < 0 (negative k).
Solve
Intercepts of an Equation
x-intercepts
Set y = 0; solve for x
Properties of Equality
Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
y-intercepts
Set x = 0; solve for y
If c is a positive number:
If
, then 2 real unequal solutions
Symmetry of the Graph of an Equation
If
, then 2 real duplicate solutions
Type
Mathematical
Geometrical
Unchanged when
If
, then no real solutions
Unchanged when
x-axis
reflected about
Properties of Inequalities
y replaced by -y
x-axis
Factored Form for real factors:
Unchanged when
Unchanged when
y-axis
reflected about
x replaced by -x
y-axis
Unchanged when
Unchanged when
y replaced by –y &
origin
rotated 180°
Page 1
x replaced by -x
about origin
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








