Radical Expressions And Rational Exponents
ADVERTISEMENT
5.6 Radical Expressions and Rational Exponents
Algebra 2
5.6 Radical Expressions and Rational Exponents
Learning Targets
1. Find roots of perfect squares, cubes, quartics, etc.
2. Use rules of exponents to convert from radical expressions to expressions with rational exponents.
3. Use rules of exponents to convert from expressions with rational exponents to radical expressions.
You have found a lot of “square roots” in your time in a math class the last few years. Today, we would like to
find “nth roots”.
Example 1: Rewrite the English expression in math notation and simplify if possible.
a) The sixth root of 64.
b) The cube root of –125.
c) The fourth root –256.
The rules for square roots also work for nth roots.
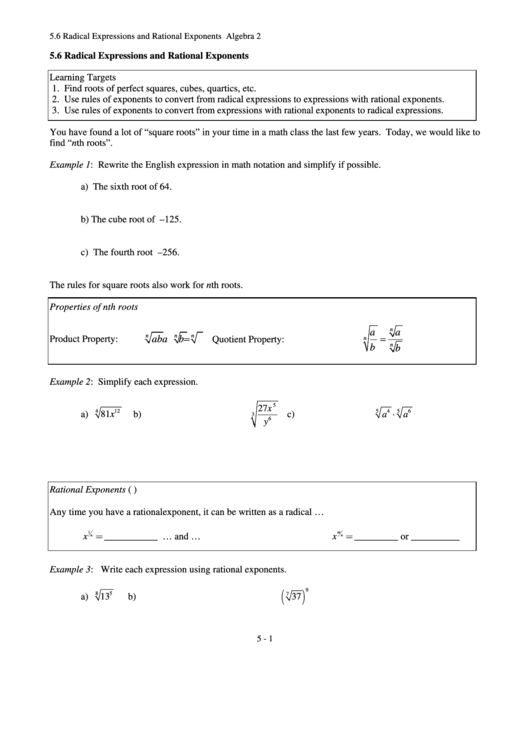
Properties of nth roots
n
a
a
=
=
n
n
n
ab
a
b
Product Property:
Quotient Property:
n
n
b
b
Example 2: Simplify each expression.
5
27x
4
12
5
4
5
6
a)
81x
b)
c)
a
a
3
6
y
Rational Exponents (a.k.a. Fractional Exponents)
Any time you have a rational exponent, it can be written as a radical …
x ___________
x _________ or __________
1
m
… and …
n
n
Example 3: Write each expression using rational exponents.
9
8
5
7
a)
b)
13
37
5 - 1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3








