Chemistry Of Macromolecules Course Outline Template
ADVERTISEMENT
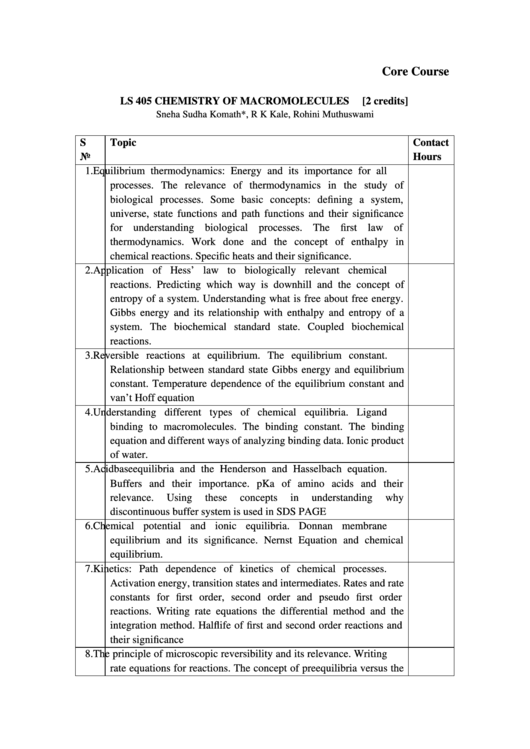
Core Course
LS 405 CHEMISTRY OF MACROMOLECULES
[2 credits]
Sneha Sudha Komath*, R K Kale, Rohini Muthuswami
S
Topic
Contact
No
Hours
1.
Equilibrium thermodynamics: Energy and its importance for all
processes. The relevance of thermodynamics in the study of
biological processes. Some basic concepts: defining a system,
universe, state functions and path functions and their significance
for understanding biological processes. The first law of
thermodynamics. Work done and the concept of enthalpy in
chemical reactions. Specific heats and their significance.
2.
Application of Hess’ law to biologically relevant chemical
reactions. Predicting which way is downhill and the concept of
entropy of a system. Understanding what is free about free energy.
Gibbs energy and its relationship with enthalpy and entropy of a
system. The biochemical standard state. Coupled biochemical
reactions.
3.
Reversible reactions at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant.
Relationship between standard state Gibbs energy and equilibrium
constant. Temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant and
van’t Hoff equation
4.
Understanding different types of chemical equilibria. Ligand
binding to macromolecules. The binding constant. The binding
equation and different ways of analyzing binding data. Ionic product
of water.
5.
Acidbaseequilibria and the Henderson and Hasselbach equation.
Buffers and their importance. pKa of amino acids and their
relevance.
Using
these
concepts
in
understanding
why
discontinuous buffer system is used in SDS PAGE
6.
Chemical potential and ionic equilibria. Donnan membrane
equilibrium and its significance. Nernst Equation and chemical
equilibrium.
7.
Kinetics: Path dependence of kinetics of chemical processes.
Activation energy, transition states and intermediates. Rates and rate
constants for first order, second order and pseudo first order
reactions. Writing rate equations the differential method and the
integration method. Halflife of first and second order reactions and
their significance
8.
The principle of microscopic reversibility and its relevance. Writing
rate equations for reactions. The concept of preequilibria versus the
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2