Covalent Bonds Form
ADVERTISEMENT
Covalent Bonds
• Atoms that are held together as result of sharing of the valence electron are bonded by
covalent bonds.
• Example Cl
2
• Single covalent bond is a bond where the atoms are held together by sharing two
electorns.
• Covalent bonds form between two atoms when ionic or metallic is unlikely because
of the loss of or gain of electrons requires large amount of energy.
• The number of valence electron and the octet rule govern the formation of most
covalent bonds.
C (Group IV)
N (Group V)
O (Group VI)
4 valence electrons
5 valence electrons
6 valence electrons
4 shared pairs
3 shared pairs
2 shared pairs
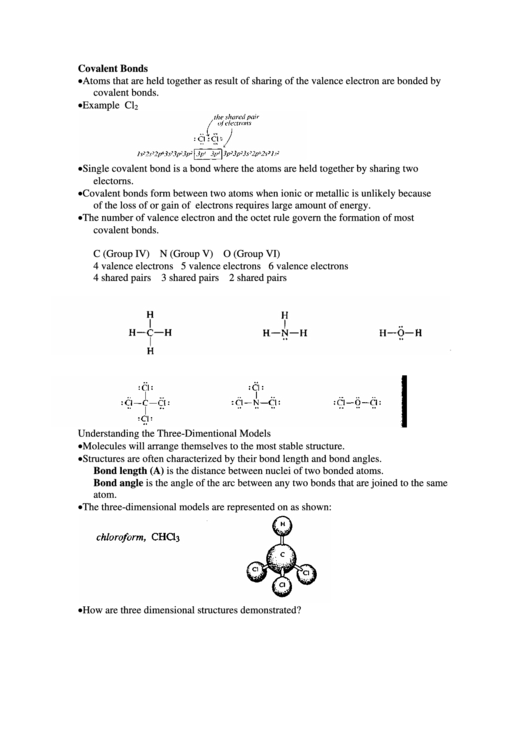
Understanding the Three-Dimentional Models
• Molecules will arrange themselves to the most stable structure.
• Structures are often characterized by their bond length and bond angles.
Bond length (A) is the distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Bond angle is the angle of the arc between any two bonds that are joined to the same
atom.
• The three-dimensional models are represented on as shown:
• How are three dimensional structures demonstrated?
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2