Extraction Of Caffeine Lab Template
ADVERTISEMENT
1
Extraction of Caffeine
Introduction
Caffeine
Caffeine occurs naturally in tea leaves and coffee beans. Cocoa beans, used to produce
chocolate, contain a compound that is nearly identical in structure to caffeine. Caffeine is also
added to many types of soda and energy drinks. Caffeine is a white solid material at room
temperature. It is classified as an alkaloid—a nitrogen-containing basic (as opposed to acidic)
compound that is obtained from plants and has physiological effects in the body. Caffeine is a
stimulant and mildly addictive. Withdrawal symptoms may include headache and irritability.
There is no conclusive evidence that caffeine causes cancer or heart disease. However, animal
studies suggest it may be a weak teratogen (an agent that causes birth defects in an embryo or
fetus), so pregnant women are advised to limit their intake of caffeinated beverages.
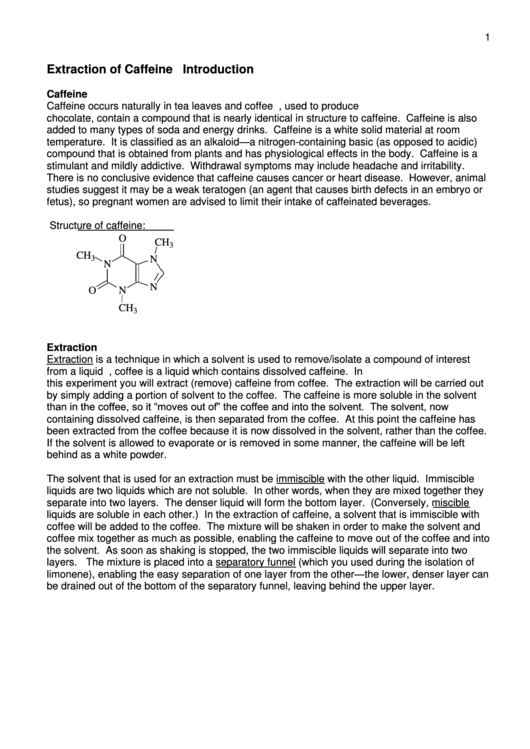
Structure of caffeine:
O
CH
3
CH
N
3
N
N
O
N
CH
3
Extraction
Extraction is a technique in which a solvent is used to remove/isolate a compound of interest
from a liquid substance. For example, coffee is a liquid which contains dissolved caffeine. In
this experiment you will extract (remove) caffeine from coffee. The extraction will be carried out
by simply adding a portion of solvent to the coffee. The caffeine is more soluble in the solvent
than in the coffee, so it “moves out of” the coffee and into the solvent. The solvent, now
containing dissolved caffeine, is then separated from the coffee. At this point the caffeine has
been extracted from the coffee because it is now dissolved in the solvent, rather than the coffee.
If the solvent is allowed to evaporate or is removed in some manner, the caffeine will be left
behind as a white powder.
The solvent that is used for an extraction must be immiscible with the other liquid. Immiscible
liquids are two liquids which are not soluble. In other words, when they are mixed together they
separate into two layers. The denser liquid will form the bottom layer. (Conversely, miscible
liquids are soluble in each other.) In the extraction of caffeine, a solvent that is immiscible with
coffee will be added to the coffee. The mixture will be shaken in order to make the solvent and
coffee mix together as much as possible, enabling the caffeine to move out of the coffee and into
the solvent. As soon as shaking is stopped, the two immiscible liquids will separate into two
layers. The mixture is placed into a separatory funnel (which you used during the isolation of
limonene), enabling the easy separation of one layer from the other—the lower, denser layer can
be drained out of the bottom of the separatory funnel, leaving behind the upper layer.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8








