Decimals With Base Ten Blocks
ADVERTISEMENT
Decimals
Objective(s): Develop multiple models to represent, compare and order decimal numbers
AZ Math Standards Performance Objectives (samples):
Strand 1: Number Sense and Operation
Concept 1: Number Sense
• Grade 3 PO 18: Order three or more decimals, through hundredths, using models,
illustrations, or symbols.
• Grade 4 PO 15: Compare two decimals
• Grade 5 PO7: Order whole numbers, fractions, and decimals.
Directions:
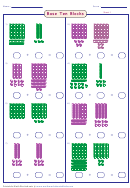
Place Value Chart: Represent the decimal point by placing the chip between the columns on the
place value chart. Construct decimals numbers using base ten blocks and this place value chart.
Example: Represent the number 2.31 using the base ten blocks or chip abacus.
or
Since our decimal point is located between the flat and the rod, the flat represents one.
1
The rod represents one-tenth of the flat which as a fraction is
and as a decimal is 0.1.
10
1
The small cube represents one one-hundredth of the flat which as a fraction is
and as
100
a decimal is 0.01. When we apply the multiplicative and additive properties of our base
ten number system, we say that the number represented in the chart
(
) (
) (
)
is
.
2
×
1
+
3
×
0
1 .
+
1
×
. 0
01
=
. 2
31
NOTE: Place values change when the decimal point is moved.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3