Working In Hot Weather Or Hot Workplace Environments
ADVERTISEMENT
Working in Hot Weather or Hot Workplace Environments
Subject: Procedures and Guidelines for Working in Hot Environments
Applies to: All employees
Number: 2010-06
Pages: 7
Effective Date: November 2010
Supersedes: June 2010
Prepared and Approved by: Occupational Health and Safety
PURPOSE:
This work procedure is intended to prevent potential heat induced illness as a result of hot
weather or hot workplace environments.
DEFINITIONS:
Acclimatization: Physiological changes which occur in response to several days of heat
exposure and make the body accustomed to a hot environment.
ACGIH - American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists
Heat stress – The sum of environmental and metabolic heat loads on the individual. Includes
heat exhaustion, heat stroke, heat rash, heat cramps and fainting.
Hot environment – Conditions that challenge the human body by subjecting it to the single or
combined effects of air temperature, sunshine, wind speed, humidity and duration of exposure.
Humidex – An index from Environmental Canada that combines the effects of temperature and
humidity to quantify human discomfort due to perceived heat.
Relative humidity – The moisture content of air expressed as a percentage of the maximum it can
hold at a given temperature, (% RH). Optimum relative humidity for comfort is between 30%
and 60%.
Temperature – Expressed in degrees Celsius (۫ C) or degrees Fahrenheit (۫ F). The optimum
temperature for comfort is 22 to 24 ۫ C. Temperature preferences can vary among individuals.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Miscellaneous
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5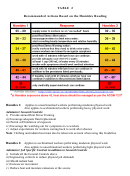 6
6 7
7








