Acute Ischemic Stroke : Infarct Core Estimation On Ct Angiography Source Images Depends On Ct Angiography Protocol Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
NEURORADIOLOGY:
Infarct Core Estimation on CT Angiography Source Images Depends on Protocol
Pulli et al
Figure 5
Figure 5: Bland-Altman plots of interrater agreement for CT angiography source images (CTA-SI) according to protocol show that (a) protocol
1 resulted in good agreement, with a mean difference of 2 2.1 mL and narrow limits of agreement (6.7, 2 11.0 mL), while with (b) protocol 2,
the mean difference was 2 7.9 mL, with limits of agreement of 16.7, 2 32.4 mL. Dotted line = line of equality.
that involve craniocaudal imaging ( 15 ),
a situation where blood fl ow via collat-
protocol that is empirically validated to
a shortened delay time ( 16 ), and in-
eral vessels is delayed. Insuffi cient de-
provide a good estimate of the infarct
creased table speed ( 32 ).
lay time is also the most likely expla-
core be established at each institution.
Our fi nding that evaluation of acute
nation for the fi ndings of Sharma et al
Unfortunately, there are trade-offs
ischemia with CT angiography source
( 18 ), who concluded that CT angiogra-
between vessel and parenchymal imag-
images is protocol dependent refl ects
phy source images appear to be CBF
ing with CT angiography. The primary
the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke.
weighted instead of CBV weighted. In
goals of our CT angiography protocol
While DW imaging images the differ-
their study, they used a 5–10-second
optimization were to speed evaluation
ences in Brownian motion of protons in
delay time, which, according to our
and to improve visualization of the in-
water, CT angiography source images
data, would be too short. In contrast,
tracranial arteries, allowing for better
provide an approximation of CBV un-
Wittkamp et al ( 33 ) triggered CT image
characterization of vessel occlusions,
der the assumption of a steady state be-
acquisition at peak enhancement of the
stenoses, and aneurysms. The longer
tween arterial and parenchymal contrast
superior sagittal sinus, ensuring suffi -
delay required for parenchymal eval-
material ( 13,14 ). Attenuation values of
cient delay times. Furthermore, they
uation would prevent vessel opacifi ca-
brain tissue on CT angiography source
performed CT angiography after perfu-
tion in the early arterial phase. To solve
images are directly proportional to the
sion CT, so that contrast material from
this problem, two protocols could be
amount of contrast material that has
the perfusion CT study had enough time
implemented, one performed early for
arrived within the parenchyma at the
to reach the ischemic bed by the time
optimal visualization of the intracranial
time of imaging. When a proximal ce-
of CT angiography image acquisition.
arteries, and a second performed with
rebral artery is occluded, the affected
As a result, they found good correla-
an appropriate delay to evaluate the
territory is supplied by the collateral
tion between CT angiography source
brain parenchyma. Our data suggest
circulation, prolonging contrast mate-
images and CBV. Results of initial studies
that a delay of at least 40 seconds may
rial arrival time even in the setting of
( 10,11 ) demonstrating a close approxi-
be suffi cient. While we found an under-
suffi cient blood fl ow. Earlier CT angi-
mation in infarct size between CT an-
estimation of DW imaging volumes us-
ography image acquisition prevents
giography source images and DW im-
ing such a delay, the differences were
contrast material from traversing the
ages also likely used a suffi cient delay
relatively small, and there remained
collateral vessels and reaching the dis-
time. The fact that this issue was not
a strong correlation between the two
tal bed, thereby increasing the area
detected earlier probably relates to the
techniques such that CT angiography
of hypoattenuation. This explains why
inability of older CT scanners to image
source images acquired with this delay
time to imaging was an independent
at speeds similar to those of current
provided a reasonable approximation of
predictor of volume overestimation on
scanners. On the basis of our fi ndings,
the infarct core.
CT angiography source images in this
we suggest that when CT angiography
Our study limitations included its
study. Similarly, atrial fi brillation, as a
source images are used to evaluate the
retrospective design. Therefore, there was
surrogate for low cardiac output, creates
parenchyma during ischemic stroke, a
a shorter time between CT angiography
601
Radiology: Volume 262: Number 2—February 2012
n
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6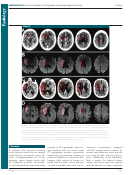 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12








