How Cells Make Protein: Translation - Biology Worksheet Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
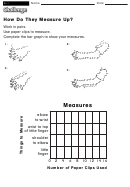
5. T
G
C
Ala= alanine
Gln = glutamine
Leu= leucine
Ser=serine
HE
ENETIC
ODE AND
Arg= arginine
Glu= glutamate
Lys= lysine
Thr=threonine
P
S
ROTEIN
YNTHESIS
Asn= asparagine
Gly = glycine
Met = methionine
Trp= tryptophan
Asp= aspartate
His= histidine
Phe= phenylalanine
Tyr = tyrosine
Cys= cysteine
Ile= isoleucine
Pro= proline
Val= valine
The central dogma of molecular genetics is DNA makes RNA makes protein . As we've seen, how this happens
involves some complicated cellular machinery, but figuring out what protein will be made from DNA or RNA is easy. It
involves reading a “genetic code dictionary.”
The dictionary is always based around RNA and its four bases A, U, C, and G. Two versions are shown below. In
either case, you always start by breaking the RNA into codons (groups of 3 bases).
Standard, Tabular Dictionary
Circular Dictionary
st
st
Find the 1
base on the left, the second base on top,
Find the 1
base in the center, the second in the
rd
and the 3
base on the right.
middle ring, and the last in the outermost ring.
Example:
Problem 1
Translate the following mRNA into protein.
mRNA:
AUG CCC AAA GGG UUU UAG
Amino
mRNA:
AUG CGU UUC GGU UAC UGA
Amino
MET ARG PHE GLY TYR STOP
acids
acids
Problem 2: Transcribe the DNA into RNA, then
Problem 3: same instructions as problem 2
translate the RNA (advice: Use lines to divide the
bases into triplets)
DNA
TACAGCCTCGACAAG
TACGCAAAGCCAATGACT
DNA
mRNA:
mRNA:
Amino
Amino
acids
acids
Problem 4: Figure out which RNA and DNA would code
Problem 5: Figure out the DNA and amino acids from
for the following sequence of amino acids (multiple
the following mRNA
DNA
answers are possible)
DNA
CUCAAGUGCUUC
mRNA:
mRNA:
Amino
Amino
GLY ASN VAL LEU CYS VAL
acids
acids
Page 2 of 8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8