1.2 Unpaired T-Tests
ADVERTISEMENT
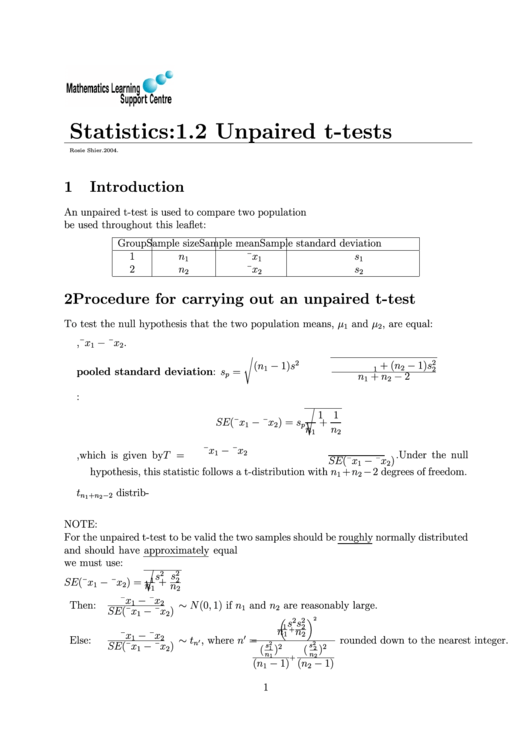
Statistics:
1.2 Unpaired t-tests
Rosie Shier. 2004.
1
Introduction
An unpaired t-test is used to compare two population means. The following notation will
be used throughout this leaflet:
Group Sample size Sample mean Sample standard deviation
1
¯
1
1
1
2
¯
2
2
2
2
Procedure for carrying out an unpaired t-test
To test the null hypothesis that the two population means,
and
, are equal:
1
2
1. Calculate the difference between the two sample means, ¯
¯
.
1
2
2
2
(
1)
+ (
1)
1
2
1
2
2. Calculate the pooled standard deviation:
=
+
2
1
2
3. Calculate the standard error of the difference between the means:
1
1
(¯
¯
) =
+
1
2
1
2
¯
¯
1
2
4. Calculate the T-statistic, which is given by
=
. Under the null
(¯
¯
)
1
2
hypothesis, this statistic follows a t-distribution with
+
2 degrees of freedom.
1
2
5. Use tables of the t-distribution to compare your value for T to the
distrib-
+
2
1
2
ution. This will give the p-value for the unpaired t-test.
NOTE:
For the unpaired t-test to be valid the two samples should be roughly normally distributed
and should have approximately equal variances. If the variances are obviously unequal
we must use:
2
2
1
2
(¯
¯
) =
+
1
2
1
2
¯
¯
1
2
Then:
(0 1) if
and
are reasonably large.
1
2
(¯
¯
)
1
2
2
2
2
1
2
+
¯
¯
1
2
1
2
Else:
, where
=
rounded down to the nearest integer.
2
2
(¯
¯
)
2
2
(
)
(
)
1
2
1
2
1
2
+
(
1)
(
1)
1
2
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3