Solution Key - 7.013 Exam 2 (4/3/13) - With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
3’
3’
Solution Key- 7.013 EXAM 2 (4 / 3 / 13)
Question 1 (20 points)
a) In the table below, name the sub-cellular location or organelle(s) of the eukaryotic cell that will
fluoresce when the following macromolecules are tagged with a fluorescent dye.
Macromolecules tagged with fluorescent dye
Sub-cellular location or organelle(s)
of cell that will fluoresce
Proteins that add carbohydrates or lipids to the newly synthesized
Golgi body, ER
proteins
Proteins that are a part of functional ribosomes
Cytoplasm & ER
DNA
Nucleus & mitochondria
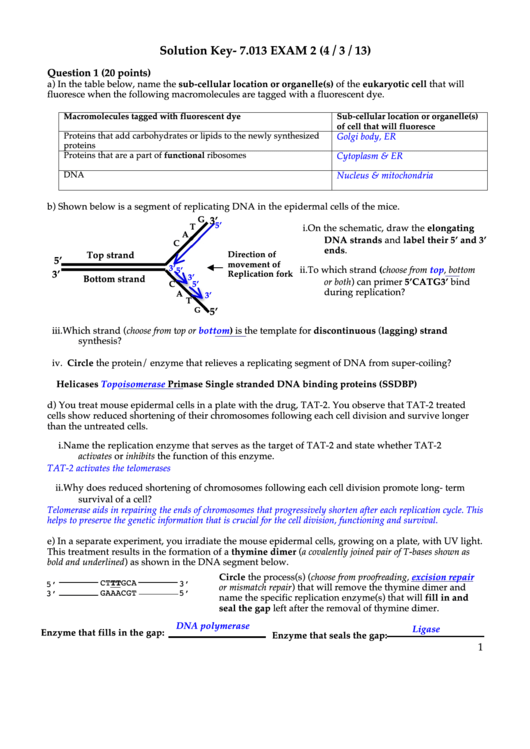
b) Shown below is a segment of replicating DNA in the epidermal cells of the mice.
G
3’
5’
T
i.
On the schematic, draw the elongating
A
DNA strands and label their 5’ and 3’
C
ends.
Top strand
Direction of
5’
movement of
3’
5’
ii.
To which strand (choose from top, bottom
3’
Replication fork
3’
Bottom strand
or both) can primer 5’CATG3’ bind
C
5’
during replication?
A
3’
T
G
5’
iii.
Which strand (choose from top or bottom) is the template for discontinuous (lagging) strand
synthesis?
iv.
Circle the protein/ enzyme that relieves a replicating segment of DNA from super-coiling?
Helicases
Topoisomerase
Primase
Single stranded DNA binding proteins (SSDBP)
d) You treat mouse epidermal cells in a plate with the drug, TAT-2. You observe that TAT-2 treated
cells show reduced shortening of their chromosomes following each cell division and survive longer
than the untreated cells.
i.
Name the replication enzyme that serves as the target of TAT-2 and state whether TAT-2
activates or inhibits the function of this enzyme.
TAT-2 activates the telomerases
ii.
Why does reduced shortening of chromosomes following each cell division promote long- term
survival of a cell?
Telomerase aids in repairing the ends of chromosomes that progressively shorten after each replication cycle. This
helps to preserve the genetic information that is crucial for the cell division, functioning and survival.
e) In a separate experiment, you irradiate the mouse epidermal cells, growing on a plate, with UV light.
This treatment results in the formation of a thymine dimer (a covalently joined pair of T-bases shown as
bold and underlined) as shown in the DNA segment below.
Circle the process(s) (choose from proofreading,
excision repair
CTTTGCA
3’
5’
or mismatch repair) that will remove the thymine dimer and
GAAACGT
3’
5’
name the specific replication enzyme(s) that will fill in and
seal the gap left after the removal of thymine dimer.
DNA polymerase
Ligase
Enzyme that fills in the gap:
Enzyme that seals the gap:
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7