Blood Test Results Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
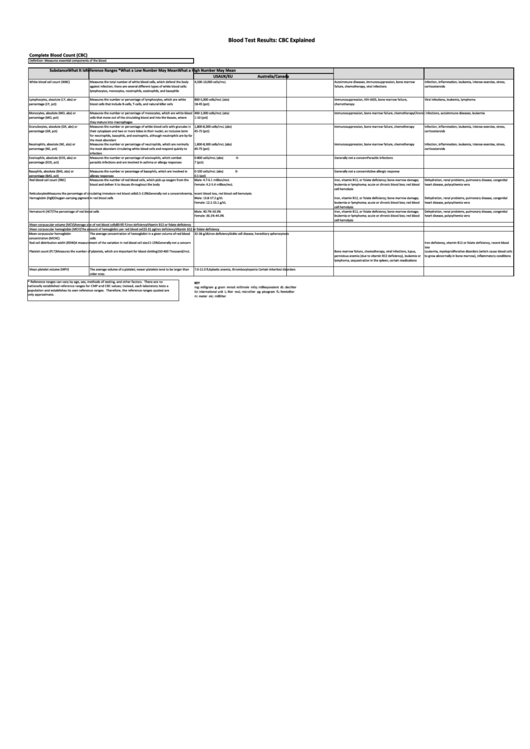
Blood Test Results: CBC Explained
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Definition: Measures essential components of the blood
Substance
What It Is
Reference Ranges *
What a Low Number May Mean
What a High Number May Mean
USA
UK/EU
Australia/Canada
White blood cell count (WBC)
Measures the total number of white blood cells, which defend the body
4,500-10,000 cells/mcL
Autoimmune diseases, immunosuppression, bone marrow
Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
against infection; there are several different types of white blood cells:
failure, chemotherapy, viral infections
corticosteroids
lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
Lymphocytes, absolute (LY, abs) or
Measures the number or percentage of lymphocytes, which are white
800-5,000 cells/mcL (abs)
Immunosuppression, HIV-AIDS, bone marrow failure,
Viral infections, leukemia, lymphoma
percentage (LY, pct)
blood cells that include B-cells, T-cells, and natural killer cells
18-45 (pct)
chemotherapy
Monocytes, absolute (MO, abs) or
Measures the number or percentage of monocytes, which are white blood
400-1,000 cells/mcL (abs)
Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy
Chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, leukemia
percentage (MO, pct)
cells that move out of the circulating blood and into the tissues, where
1-10 (pct)
they mature into macrophages
Granulocytes, absolute (GR, abs) or
Measures the number or percentage of white blood cells with granules in
1,800-8,300 cells/mcL (abs)
Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy
Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
percentage (GR, pct)
their cytoplasm and two or more lobes in their nuclei; an inclusive term
45-75 (pct)
corticosteroids
for neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils, although neutrophils are by far
the most abundant
Neutrophils, absolute (NE, abs) or
Measures the number or percentage of neutrophils, which are normally
1,800-8,300 cells/mcL (abs)
Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy
Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
percentage (NE, pct)
the most abundant circulating white blood cells and respond quickly to
45-75 (pct)
corticosteroids
infection
Eosinophils, absolute (EOS, abs) or
Measures the number or percentage of eosinophils, which combat
0-800 cells/mcL (abs)
0-
Generally not a concern
Parasitic infections
percentage (EOS, pct)
parasitic infections and are involved in asthma or allergy responses
7 (pct)
Basophils, absolute (BAS, abs) or
Measures the number or pecentage of basophils, which are involved in
0-100 cells/mcL (abs)
0-
Generally not a concern
Active allergic response
percentage (BAS, pct)
allergy responses
0.5 (pct)
Red blood cell count (RBC)
Measures the number of red blood cells, which pick up oxygen from the
Male: 4.7-6.1 million/mcL
Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage;
Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
blood and deliver it to tissues throughout the body
Female: 4.2-5.4 million/mcL
leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood
heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Reticulocytes
Measures the percentage of circulating immature red blood cells
0.5-2.0%
Generally not a concern
Anemia, recent blood loss, red blood cell hemolysis
Hemoglobin (HgB)
Oxygen-carrying pigment in red blood cells
Male: 13.8-17.2 g/dL
Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage;
Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
Female: 12.1-15.1 g/dL
leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood
heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Hematocrit (HCT)
The percentage of red blood cells
Male: 40.7%-50.3%
Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage;
Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
Female: 36.1%-44.3%
leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood
heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Average size of red blood cells
80-95 fL
Iron deficiency
Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
The amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell
23-31 pg
Iron deficiency
Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin
The average concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of red blood
32-36 g/dL
Iron deficiency
Sickle cell disease, hereditary spherocytosis
concentration (MCHC)
cells
Red cell distribution width (RDW)
A measurement of the variation in red blood cell size
11-15%
Generally not a concern
Iron deficiency, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, recent blood
loss
Platelet count (PLT)
Measures the number of platelets, which are important for blood clotting 150-400 Thousand/mcL
Bone marrow failure, chemotherapy, viral infections, lupus,
Leukemia, myeloproliferative disorders (which cause blood cells
pernicious anemia (due to vitamin B12 deficiency), leukemia or
to grow abnormally in bone marrow), inflammatory conditions
lymphoma, sequestration in the spleen, certain medications
Mean platelet volume (MPV)
The average volume of a platelet; newer platelets tend to be larger than
7.0-11.0 fL
Aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia
Certain inherited disorders
older ones
* Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no
KEY
nationally established reference ranges for CMP and CBC values; instead, each laboratory tests a
mg: milligram g: gram mmol: millimole mEq: milliequivalent dL: deciliter
population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are
IU: international unit L: liter mcL: microliter pg: picogram fL: femtoliter
only approximate.
m: meter mL: milliliter
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1