Buffer Solutions Worksheet With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
Buffer Calculations
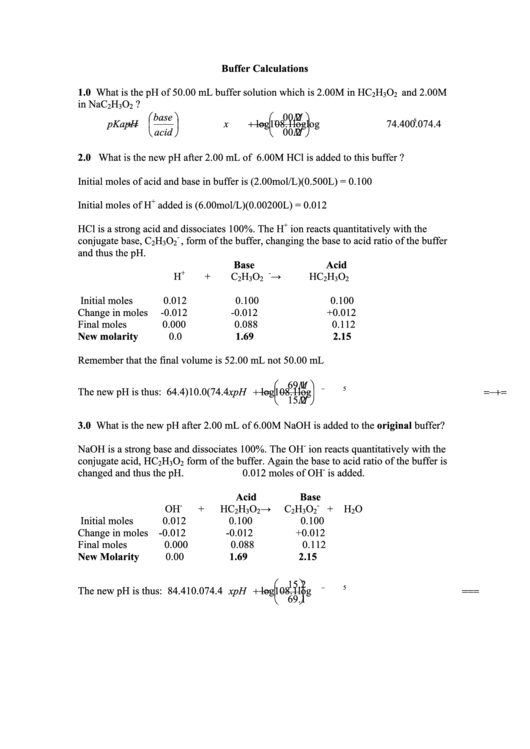
1.0 What is the pH of 50.00 mL buffer solution which is 2.00M in HC
H
O
and 2.00M
2
3
2
in NaC
H
O
?
2
3
2
base
. 2
00
M
=
+
=
−
−
+
=
+
=
5
pH
pKa
log
log
1
8 .
x
10
log
. 4
74
. 0
00
. 4
74
acid
. 2
00
M
2.0 What is the new pH after 2.00 mL of 6.00M HCl is added to this buffer ?
Initial moles of acid and base in buffer is (2.00mol/L)(0.500L) = 0.100
+
Initial moles of H
added is (6.00mol/L)(0.00200L) = 0.012
+
HCl is a strong acid and dissociates 100%. The H
ion reacts quantitatively with the
-
conjugate base, C
H
O
, form of the buffer, changing the base to acid ratio of the buffer
2
3
2
and thus the pH.
Base
Acid
+
-
H
+
C
H
O
→
HC
H
O
2
3
2
2
3
2
Initial moles
0.012
0.100
0.100
Change in moles
-0.012
-0.012
+0.012
Final moles
0.000
0.088
0.112
New molarity
0.0
1.69
2.15
Remember that the final volume is 52.00 mL not 50.00 mL
. 1
69
M
−
=
−
+
=
+
−
=
5
The new pH is thus:
pH
log
1
8 .
x
10
log
. 4
74
(
. 0
10
)
. 4
64
. 2
15
M
3.0 What is the new pH after 2.00 mL of 6.00M NaOH is added to the original buffer?
-
NaOH is a strong base and dissociates 100%. The OH
ion reacts quantitatively with the
conjugate acid, HC
H
O
form of the buffer. Again the base to acid ratio of the buffer is
2
3
2
-
changed and thus the pH.
0.012 moles of OH
is added.
Acid
Base
-
-
OH
+
HC
H
O
→
C
H
O
+ H
O
2
3
2
2
3
2
2
Initial moles
0.012
0.100
0.100
Change in moles -0.012
-0.012
+0.012
Final moles
0.000
0.088
0.112
New Molarity
0.00
1.69
2.15
. 2
15
−
=
−
+
=
=
=
5
The new pH is thus:
pH
log
1
8 .
x
10
log
. 4
74
. 0
10
. 4
84
. 1
69
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1








