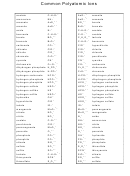
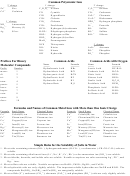
Commonly Abused Drugs Chart - National Institute On Drug Abuse - 2018
ADVERTISEMENT
Commonly Abused Drugs
Most drugs of abuse can alter a person's thinking and judgment, leading to health risks, including addiction, drugged
driving, and infectious disease. Most drugs could potentially harm an unborn baby; pregnancy-related issues are listed in
the chart below for drugs where there is enough scientific evidence to connect the drug use to specific negative effects.
For information about treatment options for drug addiction, see
NIDA’s Treatment
pages. For drug use trends, see
our
Trends and Statistics
page.
The following drugs are included in this resource:
➢ Alcohol
➢ Methamphetamine
➢ Ayahuasca
➢ Over-the-Counter Medicines--Dextromethorphan
(DXM)
➢ Central Nervous System Depressants
➢ Over-the-Counter Medicines--Loperamide
➢ Cocaine
➢ PCP
➢ DMT
➢ Prescription Opioids
➢ GHB
➢ Prescription Stimulants
➢ Hallucinogens
➢ Psilocybin
➢ Heroin
➢ Rohypnol® (Flunitrazepam)
➢ Inhalants
➢ Salvia
➢ Ketamine
➢ Steroids (Anabolic)
➢ Khat
➢ Synthetic Cannabinoids
➢ Kratom
➢ Synthetic Cathinones ("Bath Salts")
➢ LSD
➢ Tobacco
➢ Marijuana (Cannabis)
➢ MDMA (Ecstasy/Molly)
➢ Mescaline (Peyote)
**
The Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) schedule indicates the drug’s acceptable medical use and its potential for abuse
or dependence. The most up-to-date scheduling information can be found on the
DEA
website.
January 2018
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3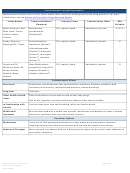 4
4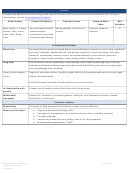 5
5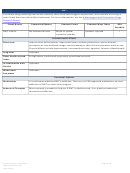 6
6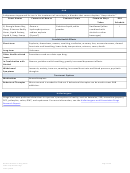 7
7 8
8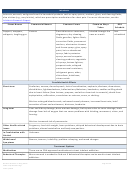 9
9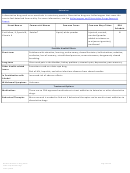 10
10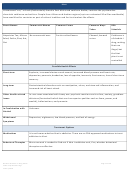 11
11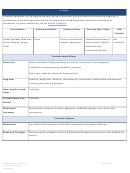 12
12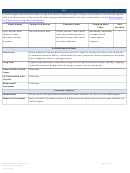 13
13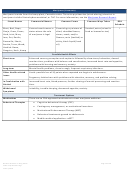 14
14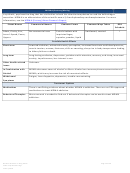 15
15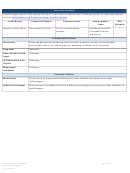 16
16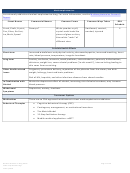 17
17 18
18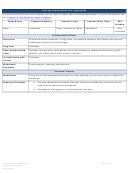 19
19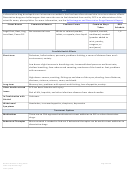 20
20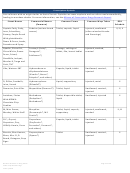 21
21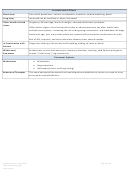 22
22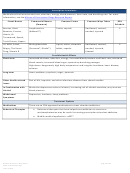 23
23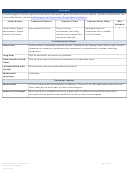 24
24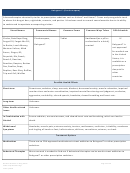 25
25 26
26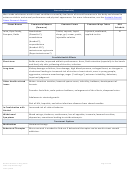 27
27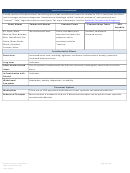 28
28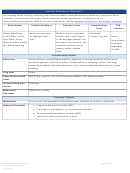 29
29 30
30