Nervous System Practice Test Template
ADVERTISEMENT
N E R V O U S S Y S T E M
B
1.
Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle
tissue D. movement of food through the intestines
B
2.
Which of the components of the nervous system has both autonomic and somatic divisions? A. Central. B. Peripheral. C. Sympathetic. D. Parasympathetic.
A
3.
The central nervous system includes the A. brain and spinal cord. B. somatic nervous system. C. cranial and spinal nerves. D. parasympathetic nervous
system.
D
4.
The somatic nervous system controls A. peristalsis. B. cardiac muscles. C. smooth muscles. D. skeletal muscles.
D
5.
Which of the following is involved in the initiation of a “fight or flight” response? A. Thyroid gland. B. Prostate gland. C. Adrenal cortex. D. Adrenal medulla.
C
6.
The part of a sensory neuron that transmits nerve impulses from a receptor to the cell body is the A. axon. B. synapse. C. dendrite. D. neurotransmitter.
B
7.
What type of neuron transmits an impulse to the central nervous system? A. Motor. B. Sensory. C. Efferent. D. Interneuron.
A
8.
The type of neuron that can only be found in the central nervous system (CNS) is a(n) A. interneuron. B. motor neuron. C. mixed neuron. D. sensory neuron.
A
9.
The type of neuron that is found only in the central nervous system is the A. interneuron. B. motor neuron. C. mixed neuron. D. sensory neuron.
D
10.
Which of the following is responsible for transmitting impulses to the central nervous system (CNS)? A. Effectors. B. Interneurons. C. Motor neurons. D.
Sensory neurons.
B
11.
Sensory neurons carry messages to A. glands. B. interneurons. C. sense organs. D. muscle fibres.
C
12.
Sensory receptors initiate nerve impulses in A. long axons. B. short axons. C. long dendrites. D. short dendrites.
D
13.
Which of the following is a characteristic of a resting potential? A. secretion of calcium ions B. neurotransmitters move into the axon
C. depolarization of the post-synaptic membrane D. a net negative charge on the inside of the axon
C
14.
During which stage of a nerve impulse does the opening of the sodium gates play an important role?
A. Recovery. B. Repolarization. C. Depolarization. D. Resting potential.
D
15.
Resting potential in a neuron is maintained by A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. pinocytosis. D. active transport.
C
16.
Which organelle would be required in large numbers by a cell whose membrane is often depolarized? A. Ribosome. B. Lysosome. C. Mitochondrion. D.
Endoplasmic reticulum.
B
17.
Within an axon, an increased concentration of sodium ions and a decreased concentration of potassium ions is observed during A. upswing. B. downswing. C.
resting potential. D. synaptic transmission.
B
18.
The resting potential in a neuron is maintained by A. exocytosis. B. active transport. C. passive diffusion. D. facilitated transport.
C
19.
The correct sequence for the transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron is 1. Potassium gates open. 2. Sodium ions diffuse into neuron. 3. Resting
potential. 4. Recovery. A. 1, 2, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 3, 2, 1, 4 D. 4, 3, 1, 2
C
20.
The correct sequence for the transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron is 1. Potassium gates open. 2. Sodium ions diffuse into neuron. 3. Resting
potential. 4. Recovery.
A. 1, 2, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 3, 2, 1, 4 D. 4, 3, 1, 2
B
21.
Nerve cells are called A. axons. B. neurons. C. dendrites. D. meninges.
B
22.
Depolarization of a nerve cell is caused by A. the sodium potassium pump. B. sodium ions entering the cell. C. the opening of the potassium gates. D. a return
of membrane potential to -60mV.
A
23.
Depolarization of an axon results from the movement of A. sodium ions. B hydrogen ions. C. potassium ions. D. bicarbonate ions.
D
24.
The distribution of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane of an axon is maintained by A. diffusion. B. exocytosis. C. phagocytosis. D. active
transport.
D
25.
Which of the following best describes the location of ions during resting potential?
A. A low concentration of sodium ions on the outside, and a high concentration of potassium ions on the inside of the neuron.
B. A low concentration of sodium ions on the outside, and a low concentration of potassium ions on the inside of the neuron.
C. A high concentration of sodium ions on the outside, and a low concentration of potassium ions on the inside of the neuron.
D. A high concentration of sodium ions on the outside, and a high concentration of potassium ions on the inside of the neuron.
C
26.
The distribution of sodium and potassium ions during resting potential is maintained by A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. active transport. D. facilitated transport.
A
27.
Use the following information to answer the question. 1. Sodium ions move into the axon. 2. Potassium ions move out of the axon. 3. Depolarization of the
membrane occurs. 4. Repolarization of the membrane occurs. Select the correct order of the above events to describe an action potential.
A. 1, 3, 2, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 3, 2, 4, 1 D. 1, 4, 3, 2
C
28.
The speed of a nerve impulse along a sensory neuron depends on the A. dendrites. B. cell bodies. C. myelin sheath. D. sensory receptors.
D
29.
The myelin sheath is a protective covering that surrounds A. only motor neurons. B. all types of neurons. C. only sensory neurons. D. both motor and sensory
neurons.
D
30.
Which of the following most accurately describes the function of the nodes of Ranvier? A. Release neurotransmitters. B. Nourish and protect the neuron. C.
Cause the ‘all or none’ response. D. Speed the transmission of nerve impulses.
A
31.
In order for a nerve impulse to pass from one neuron to the next, which of the following ions must be present at the pre-synaptic ending? A. Calcium (Ca
) . B.
2+
Chloride (Cl
) . C. Phosphate (PO
) . D. Magnesium (Mg
) .
-
4 3-
2+
A
32.
Using the information below, what is the correct order for the transmission of an impulse across a synapse? 1. Calcium interacts with proteins. 2. Vesicles fuse
with synaptic membrane. 3. Neurotransmitter diffuses into synaptic cleft. 4. Receptor sites are occupied. A. 1, 2, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 1, 4 C. 3, 2, 1, 4 D. 4, 1, 3, 2
B
33.
At a synapse, the neurotransmitters move to the receptor sites by A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. active transport. D. facilitated transport.
B
34.
At a synapse, the neurotransmitters move to the receptor sites by A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. active transport. D. facilitated transport.
B
35.
34. The function of enzymes in the synaptic cleft is to ensure that A. neurotransmitters are released.
B. neurotransmitters are destroyed. C. nerve impulses reach receptor sites. D. nerve impulses travel in both directions.
B
36.
The neurotransmitter used by the sympathetic nervous system is A. gastrin. B. noradrenalin. C. acetylcholine. D. acetylcholinesterase.
A
37.
Once a neurotransmitter has been released, it has only a short time to act because A. enzymes inactivate it. B. receptor sites break down. C. calcium ions flow
into the cleft. D. the postsynaptic membrane closes.
D
38.
Nerve impulses are not continuously generated at a synapse because A. there are insufficient calcium ions.
B. the presynaptic membrane is depolarized. C. the synaptic membranes become impermeable. D. neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes.
C
39.
In an axon, the nerve impulses normally travel A. in both directions. B. toward the cell body. C. away from the cell body. D. faster as they are unmyelinated.
D
40.
Which of the following substances would not be found in synaptic clefts? A. Noradrenalin. B. Acetylcholine. C. Cholinesterase. D. Carbonic anhydrase.
D
41.
Use the following information to answer the question: 1. Axon 2. Dendrite 3. Cell body 4. Receptor
The correct order for the transmission of an impulse along a sensory neuron is A. 3, 1, 4, 2 B. 3, 2, 1, 4 C. 4, 1, 3, 2 D. 4, 2, 3, 1
C
42.
Nerve impulses travel in only one direction because of the location of the A. effectors. B. myelin sheath. C. synaptic vesicles. D. nodes of Ranvier.
B
43.
The speed of nerve impulse conduction is increased by the presence of A. axons. B. myelin. C. dendrites. D. cell bodies.
D
44.
Transmission across a synapse is one-way because A. the axon is myelinated. B. the potassium gates are open. C. the interior of the axon contains negative
ions. D. the receptor sites are on the postsynaptic membrane.
A
45.
Neurotransmitters may create an action potential when they A. fit into receptor sites. B. move through protein pores. C. are broken down in the synapse. D.
excite the presynaptic membrane.
C
46.
A pesticide that destroys an enzyme found in the synaptic cleft may cause A. denaturation of the presynaptic contractile proteins. B. an increased rate of
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4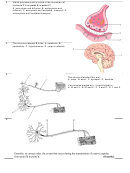 5
5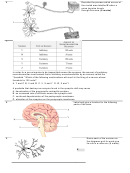 6
6 7
7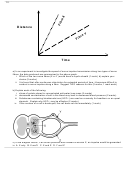 8
8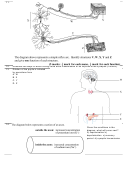 9
9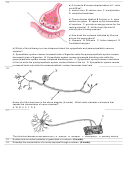 10
10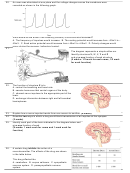 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16