Bonding Concepts Worksheet - Unit 8/9, Michalek Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
AP Chemistry - Michalek
3
Unit 08 Bonding Concepts
8.1 Notes
Bond Energy is the energy required to break a bond. Ionic Bonding is a bonding force that forms a great thermal stability
results from the electrostatic attractions of the closely packed, oppositely charged ions. Ionic compound results when
cations react with anions.
Coulomb’s Law
The energy of interactions between a pair of ions
-19
k = 2.31 x 10
J*nm, E is energy, r is the distance between ion centers, Q
1
and Q
is the ionic charge.
2
Example
In solid sodium chloride the distance between the centers is 2.76 A. What is the energy of interaction between the pairs
of ions?
If the sign is negative, the ion pair has a lower energy than the separated ions. This means a bond will form. Chemicals
are most stable in the lowest energy form. This law can also be used to calculate the repulsive energy when two like
charged ions are brought together. A bond will form if the energy of the aggregate is lower than that of the separated
atoms.
Bond length
The system will act to minimize the sum of the positive (repulsive) energy term and the negative (attractive) energy
term. The distance where the energy is at a minimum is called bond length. In covalent bonding the electrons are being
shared by the nuclei. Polar covalent bond share electron unequally; meaning that the electrons are pulled closer to the
most electronegative atom.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9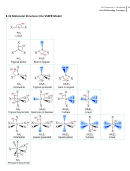 10
10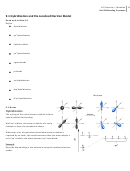 11
11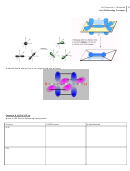 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30








