Corrective Action Plan Template And Instructions Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Enclosure 2: Instructions for Completing the Payment Error Rate Measurement (PERM)
Medicaid and CHIP Detailed Corrective Action Plan Form
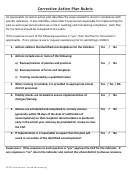
The State agency must develop a separate corrective action plan for Medicaid and CHIP
designed to reduce improper payments in each program based on its analysis of error causes in
the fee-for-service, managed care, and eligibility components. Attached are two separate detailed
corrective action plan forms, one for the Medicaid program and one for the CHIP program.
Line-by-Line Instructions: Complete one form for each component of each program.
Line A: Enter the name of the State submitting this report. Enter the Federal fiscal year in
which the State is being measured in the PERM program. This should be the same year for
which the corrective action plan addresses.
Line B: Enter the name, phone number and e-mail address of the State person assigned as the
contact person for the corrective action plan.
Line C: Enter the component for which this corrective action plan reflects (i.e., fee-for-service,
managed care or eligibility).
Line D: Narrative Instructions - for each component of each program (i.e., Medicaid or
CHIP), provide a discussion of the results of following elements.
1. Data Analysis: What clusters of errors, causes, characteristics, and frequency were identified
through the data analysis? All errors should be addressed including deficiencies, technical errors,
and eligibility active and negative case errors. Describe the results of the data analysis by:
Element – specific type of classification of errors (Examples are MR1- no
documentation and MR2- insufficient documentation)
Nature – discuss what was causing the errors
2. Program Analysis: This is the most critical part of the corrective action process. Describe
why a particular program/operational procedure caused the specific error and identify the root
causes of errors (e.g., provider manuals are unclear or outdated; eligibility staff needs training on
application of earned income).
3. Corrective Action Planning: Describe the corrective action initiatives to be implemented
and how they will reduce or eliminate the improper payments. Based on the data and program
analysis, States must determine what corrective actions are to be implemented. States must
address each payment error, deficiency/technical error, and case error, however, it remains the
State’s decision which corrective actions they take to decrease or eliminate errors. It may not be
cost effective to implement corrective actions for each and every error. States are encouraged to
use the most cost effective corrective actions that can be implemented, to best correct and
address the root causes of the errors. A cost benefit analysis will aid the State in calculating the
total expected cost of corrective actions against the benefits of corrective actions. If the State
determines that the cost of implementing a corrective action outweighs the benefits then the final
decision of implementing the corrective action is the State’s decision. The cost benefit analysis
4
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11