Shapes, And Bond Angles Of Molecules Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers
The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and pH) and physical properties (e.g. mpt and
bpt). A negative charge center or region refers to the number of pairs electrons around the central bonded atom. This includes both the lone
(non bonding pairs) pairs and bonded pairs of electrons in single, double or triple bonds. Each double and triple bond counts as one negative
charge center. Watch out for non octet examples.
Shape with respect to the
Number of negative
Bond Angle with respect
number of negative charged
charge centers
to negative charge centers
centers
2
Linear
180°
3
Trigonal planar
120°
4
Tetrahedral
109.5°
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR)
GN Lewis proposed that chemical bonds resulted when two atoms shared a pair of electrons. The Lewis concept allowed for "electron dot
bookkeeping" in the form of a Lewis dot digram to show how atoms could share electrons to achieve their quota as a noble gas or an octet of
electrons. Lewis originally did not set out to describe the shape of the molecule but it soon became apparent to him that the electron pairs
around the central atom, being like charged, would repel each other. This lead to his VSEPR theory which is still used today to describe the
shape of a molecule.
In VSEPR theory lone pairs of electrons are closer to the central atom and therefore closer to one another than the bonding pairs of electrons
because they are being attracted by the positive protons in the nucleus of one atom instead of two. The lone pairs and bonding pairs of
electrons are arranged around the central atom so as to minimize the repulsion between the lone and bonding pairs of electrons. The relative
magnitude of the electron pair repulsions is:
Lone pair / lone pair > bonded pair / lone pair > bonded pair / bonded pair repulsion
The overall shape according to the VSEPR theory depends on the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom
of a molecule. The overall bond angle is the angle between the bonded atoms attached to the central atom.
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10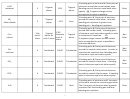 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14








