Chapter 11 Mensuration - Shapes Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
M
169
ENSURATION
CHAPTER
11
Mensuration
11.1 Introduction
We have learnt that for a closed plane figure, the perimeter is the distance around its
boundary and its area is the region covered by it. We found the area and perimeter of
various plane figures such as triangles, rectangles, circles etc. We have also learnt to find
the area of pathways or borders in rectangular shapes.
In this chapter, we will try to solve problems related to perimeter and area of other
plane closed figures like quadrilaterals.
We will also learn about surface area and volume of solids such as cube, cuboid and
cylinder.
11.2 Let us Recall
Let us take an example to review our previous knowledge.
This is a figure of a rectangular park (Fig 11.1) whose length is 30 m and width is 20 m.
(i) What is the total length of the fence surrounding it? To find the length of the fence we
need to find the perimeter of this park, which is 100 m.
(Check it)
(ii) How much land is occupied by the park? To find the
land occupied by this park we need to find the area of
2
this park which is 600 square meters (m
) (How?).
(iii) There is a path of one metre width running inside along
the perimeter of the park that has to be cemented.
2
If 1 bag of cement is required to cement 4 m
area, how
many bags of cement would be required to construct the
Fig 11.1
cemented path?
area of the path
We can say that the number of cement bags used =
.
area cemented by 1 bag
Area of cemented path = Area of park – Area of park not cemented.
2
Path is 1 m wide, so the rectangular area not cemented is (30 – 2) × (20 – 2) m
.
2
That is 28 × 18 m
.
Hence number of cement bags used = ------------------
(iv) There are two rectangular flower beds of size 1.5 m × 2 m each in the park as
shown in the diagram (Fig 11.1) and the rest has grass on it. Find the area covered
by grass.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4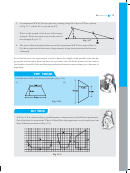 5
5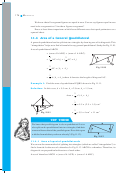 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13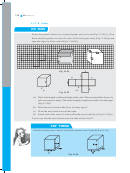 14
14 15
15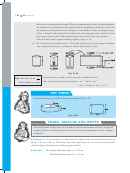 16
16 17
17 18
18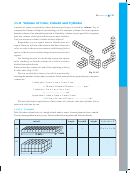 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24