Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function
ADVERTISEMENT
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry: Shape Determines Function
Problems: 9.1-9.32, 9.37, 9.39-9.65, 9.70, 9.83-9.84, 9.87-9.90, 9.95, 9.101,9.103, 9.107, 9.109, 9.120, 9.125
9.1 MOLECULAR SHAPE
Molecular Geometry (or Shape)
– the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules
– responsible for many physical and chemical properties of molecules
9.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)
Repulsion between electrons causes them to be as far apart as possible
a molecule’s shape results from the electrons on its central atom orienting themselves to
→
be as far away from each other as possible
Determining the shapes of molecules
– If there are only two atoms, the molecule must be linear.
– If there are more than two atoms in the molecule
→ the shape depends on number of electrons around the central atom
– The electrons orient themselves to maximize the distance between them.
The steric number (SN) of the central atom allows us to determine the shape of the molecule.
#
of
atoms
bonded
#
of
lone
pairs
⎛
⎞
⎛
⎞
steric number =
+
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎟
to
the
central
atom
on
the
central
atom
⎝
⎠
⎝
⎠
CENTRAL ATOMS WITH NO LONE PAIRS
Molecule #1:
BeH
2
a. Draw the Lewis structure below.
b. Draw each bonding pair of electrons as a stick,
maximizing the distance between the electron
pairs, then draw the outer atoms as balls.
Lewis structure
Be
c. The shape of the BeH
molecule is _________________ and its bond angle is _________.
2
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
1
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9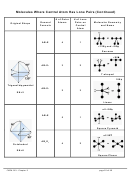 10
10 11
11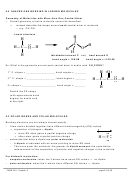 12
12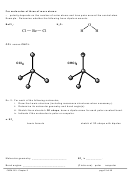 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19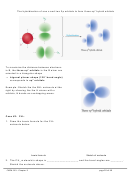 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33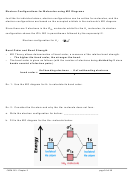 34
34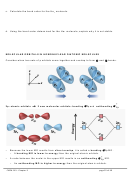 35
35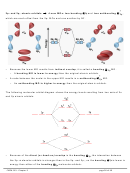 36
36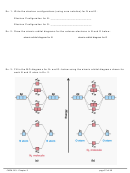 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40