Chemistry Cheat Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
mass is the amount of something...
weight is how much gravity is pulling on the mass.
(Weight will be proportional to the mass at a given spot.)
Mass is what we REALLY want to use... measured in grams.
4 • Matter
You use a balance to measure mass... you compare your
Mass & Weight -- Two Properties of Matter
object with objects of known mass.
(1 of 8)
Weight is measured with a scale (like your bathroom scale
or the scale at the grocery store). If there is no gravity, it
doesn’t work. Note: electronic balances are really scales!
1 kg
2.205 lbs
You convert mass / weight using:
or
2.205 lbs
1 kg
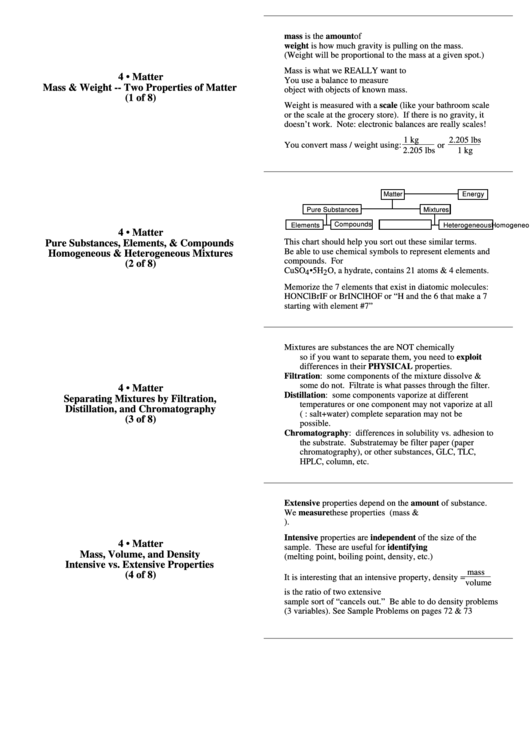
Matter
Energy
Pure Substances
Mixtures
Compounds
Elements
Homogeneous
Heterogeneous
4 • Matter
This chart should help you sort out these similar terms.
Pure Substances, Elements, & Compounds
Be able to use chemical symbols to represent elements and
Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures
compounds. For example...
(2 of 8)
CuSO
•5H
O, a hydrate, contains 21 atoms & 4 elements.
4
2
Memorize the 7 elements that exist in diatomic molecules:
HONClBrIF or BrINClHOF or “H and the 6 that make a 7
starting with element #7”
Mixtures are substances the are NOT chemically combined...
so if you want to separate them, you need to exploit
differences in their PHYSICAL properties.
Filtration: some components of the mixture dissolve &
some do not. Filtrate is what passes through the filter.
4 • Matter
Distillation: some components vaporize at different
Separating Mixtures by Filtration,
temperatures or one component may not vaporize at all
Distillation, and Chromatography
(e.g.: salt+water) complete separation may not be
(3 of 8)
possible.
Chromatography: differences in solubility vs. adhesion to
the substrate. Substratemay be filter paper (paper
chromatography), or other substances, GLC, TLC,
HPLC, column, etc.
Extensive properties depend on the amount of substance.
We measure these properties frequently... (mass &
volume... mostly).
Intensive properties are independent of the size of the
4 • Matter
sample. These are useful for identifying substances...
Mass, Volume, and Density
(melting point, boiling point, density, etc.)
Intensive vs. Extensive Properties
mass
(4 of 8)
It is interesting that an intensive property, density =
volume
is the ratio of two extensive properties... the size of the
sample sort of “cancels out.” Be able to do density problems
(3 variables). See Sample Problems on pages 72 & 73
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2