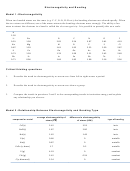
Electronegativity Difference And Bond Character
ADVERTISEMENT
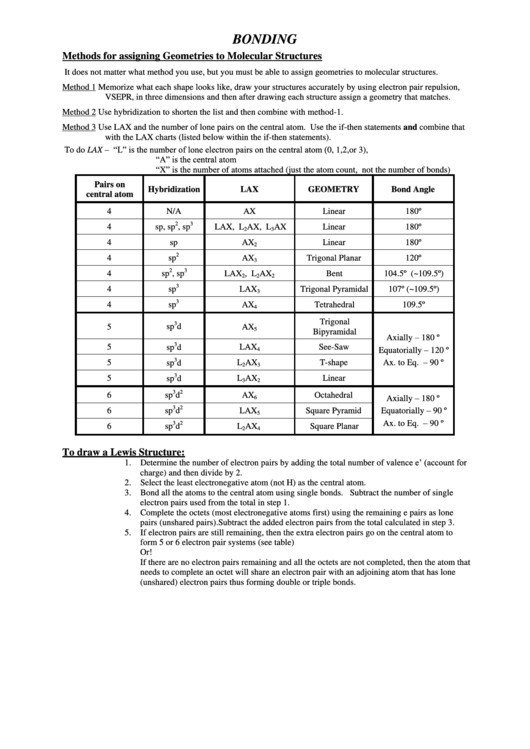
BONDING
Methods for assigning Geometries to Molecular Structures
It does not matter what method you use, but you must be able to assign geometries to molecular structures.
Method 1
Memorize what each shape looks like, draw your structures accurately by using electron pair repulsion,
VSEPR, in three dimensions and then after drawing each structure assign a geometry that matches.
Method 2
Use hybridization to shorten the list and then combine with method-1.
Method 3
Use LAX and the number of lone pairs on the central atom. Use the if-then statements and combine that
with the LAX charts (listed below within the if-then statements).
To do LAX – “L” is the number of lone electron pairs on the central atom (0, 1,2,or 3),
“A” is the central atom
“X” is the number of atoms attached (just the atom count, not the number of bonds)
Pairs on
Hybridization
LAX
GEOMETRY
Bond Angle
central atom
4
N/A
AX
Linear
180º
2
3
4
sp, sp
, sp
LAX, L
AX, L
AX
Linear
180º
2
3
4
sp
AX
Linear
180º
2
2
4
sp
AX
Trigonal Planar
120º
3
2
3
4
sp
, sp
LAX
, L
AX
Bent
104.5º (~109.5º)
2
2
2
3
4
sp
LAX
Trigonal Pyramidal
107º (~109.5º)
3
3
4
sp
AX
Tetrahedral
109.5º
4
Trigonal
3
5
sp
d
AX
5
Bipyramidal
Axially – 180 º
3
5
sp
d
LAX
See-Saw
Equatorially – 120 º
4
3
Ax. to Eq. – 90 º
5
sp
d
L
AX
T-shape
2
3
3
5
sp
d
L
AX
Linear
3
2
3
2
6
sp
d
AX
Octahedral
Axially – 180 º
6
3
2
Equatorially – 90 º
6
sp
d
LAX
Square Pyramid
5
Ax. to Eq. – 90 º
3
2
6
sp
d
L
AX
Square Planar
2
4
To draw a Lewis Structure:
Determine the number of electron pairs by adding the total number of valence e’ (account for
1.
charge) and then divide by 2.
2.
Select the least electronegative atom (not H) as the central atom.
3.
Bond all the atoms to the central atom using single bonds. Subtract the number of single
electron pairs used from the total in step 1.
4.
Complete the octets (most electronegative atoms first) using the remaining e pairs as lone
pairs (unshared pairs). Subtract the added electron pairs from the total calculated in step 3.
5.
If electron pairs are still remaining, then the extra electron pairs go on the central atom to
form 5 or 6 electron pair systems (see table)
Or!
If there are no electron pairs remaining and all the octets are not completed, then the atom that
needs to complete an octet will share an electron pair with an adjoining atom that has lone
(unshared) electron pairs thus forming double or triple bonds.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4