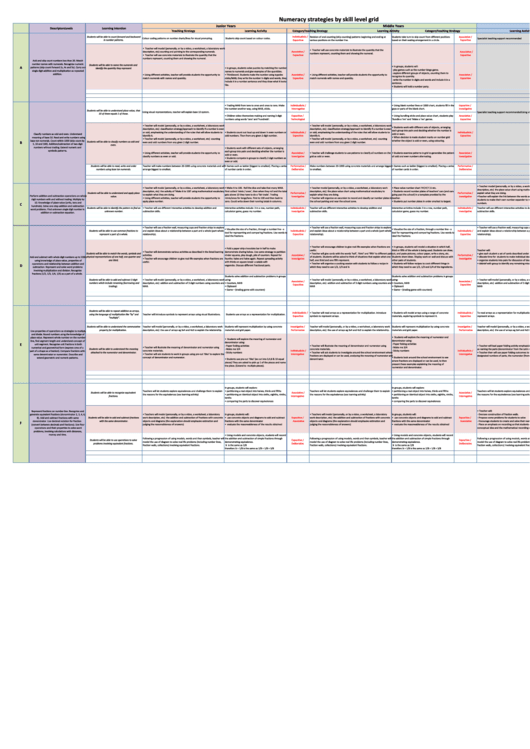
Numeracy Strategies By Skill Level Grid
ADVERTISEMENT
Numeracy strategies by skill level grid
Junior Years
Middle Years
Upper Years
Levels
Descriptors
Learning intention
Teaching Strategy
Learning Activity
Category
Teaching Strategy
Learning Activity
Category
Teaching Strategy
Learning Activity
Category
Students will be able to count forward and backward
Individualistic /
Revision of oral counting (skip counting) patterns beginning and ending at
Students take turn to skip count from different positions
Associative /
Colour coding patterns on number charts/lines for visual prompting.
Students skip count based on colour codes.
Specialist teaching support recommended
in number patterns.
Expositive
various positions on the number line.
based on their seating arrangement in a circle.
Expositive
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Teacher will use concrete materials to illustrate the quantity that the
description, etc) counting and pointing to the corresponding numerals.
Associative /
Associative /
numbers represent, counting them and showing the numeral.
• Teacher will use concrete materials to illustrate the quantity that the
Expositive
Expositive
numbers represent, counting them and showing the numeral.
Add and skip count numbers less than 20. Match
number names with numerals. Recognise numeric
Students will be able to name the numerals and
• In groups, students will:
A
patterns (skip count forward 2s, 4s and 5s). Carry out
• In groups, students solve puzzles by matching the number
identify the quantity they represent
‐ play games such as the number bingo game.
single digit addition and multiplication as repeated
names to numerals and give examples of the quantities.
‐ explore different groups of objects, counting them to
addition.
• Using different activities, teacher will provide students the opportunity to
• Thinkboard. Students make the number using icypoles
Associative /
• Using different activities, teacher will provide students the opportunity to
Associative /
recognise its quantity.
match numerals with names and quantity.
sticks/MAB, they write the number in digits and words, they
Expositive
match numerals with names and quantity.
Expositive
‐ write the number in digits and words and include it in a
include it in a number sentence and they draw what it looks
sentence.
like.
• Students will hold a number party.
• Trading MAB from tens to ones and ones to tens. Make
Individualistic /
• Using blank number lines or 1000 chart, students fill in the
Expositive /
the number another way, using MAB, sticks.
Interrogative
gaps or parts of the blank chart.
Investigative
Students will be able to understand place value, that
Using visual representations, teacher will explain base 10 system.
Using visual representations, explain base 10 system.
Specialist teaching support recommended
10 of these equals 1 of those.
• Children video themselves making and naming 3‐digit
Expositive /
• Using bundling sticks and place value chart, students play
Associative /
numbers using words 'tens' and 'hundreds'.
Technological
‘Bundle a Ten’ and ‘Make a Ten’ games.
Expositive
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Students work with different sets of objects, arranging
description, etc) classification strategy/approach to identify if a number is even
description, etc) classification strategy/approach to identify if a number is even
each group into pairs and deciding whether the number is
or odd, emphasising the understanding of the rules that will allow students to
• Students count out loud up and down in even numbers or
Individualistic /
or odd, emphasising the understanding of the rules that will allow students to
Individualistic /
odd or even.
Classify numbers as odd and even. Understand
identify it.
odd numbers. Then from any given 2 digit number.
Expositive
identify it.
Expositive
meaning of base 10. Read and write numbers using
• When decision is made student marks on number grid
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, etc) counting
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, etc) counting
base ten numerals. Count within 1000 (skip count by
whether the object is odd or even, using colouring.
B
Students will be able to classify numbers as odd and
even and odd numbers from any given 2 digit number.
even and odd numbers from any given 2 digit number.
5, 10 and 100). Addition/subtraction of two digit
even.
numbers without trading. Extend numeric and
• Students work with different sets of objects, arranging
symbolic patterns.
each group into pairs and deciding whether the number is
• Using different activities, teacher will provide students the opportunity to
Associative /
• Teacher will challenge students to use patterns to classify all numbers on the
• Students examine patterns in grid to generalise the pattern
Associative /
odd or even.
classify numbers as even or odd.
Investigative
grid as odd or even.
of odd and even numbers alternating.
Investigative
• Students compete in groups to classify 2 digit numbers as
even or odd.
Students will be able to read, write and order
Teacher will make numbers between 20‐1000 using concrete materials and will
• Games such as ladder (biggest to smallest). Placing a series
Performative /
Make numbers between 20‐1000 using concrete materials and arrange biggest
• Games such as ladder (biggest to smallest). Placing a series
Performative /
numbers using base ten numerals.
arrange biggest to smallest.
of number cards in order.
Deliberative
to smallest.
of number cards in order.
Deliberative
• Teacher model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Make It to 100. Roll the dice and take that many MAB.
• Teacher model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
• Place value number chart TH|H|T|U etc.
description, etc) the place value chart using mathematical vocabulary to
description, etc) the activity of 'Make it to 100' using mathematical vocabulary
First collect ‘minis / ones’, then when they roll and the total
description, etc) the place value chart using mathematical vocabulary to
• Students record number plates of teachers’ cars (and cars
• Place value number chart TH|H|T|U etc.
Students will be able to understand and apply place
Performative /
Performative /
explain what they are doing.
Performative /
to explain what they are doing.
gets above 10 they have to do a ‘fair trade’. Trading
explain what they are doing.
going past the school) in a template provided by the
• Make their own number expander to represent large or
Perform addition and subtraction operations on whole
value.
Investigative
Investigative
•Teacher will explain the link between the words and the model, asking the
Investigative
• Using different activities, teacher will provide students the opportunity to
minis/ones for longs/tens. First to 100 and then back to
• Teacher will organise an excursion to record and classify car number plates in
teacher.
small numbers.
digit numbers with and without trading. Multiply by
students to make their own number expander to represent larger or small
apply place number.
zero. Could write down their running totals in columns.
the school parking and near the school zone.
• Students put number plates in order smallest to largest.
10. Knowledge of place value (units, tens and
numbers.
C
hundreds). Solve one step addition and subtraction
Students will be able to identify the pattern to find an
• Teacher will use different interactive activities to develop addition and
Interactive activities include: 3 in a row, number path,
Individualistic /
Teacher will use different interactive activities to develop addition and
Interactive activities include: 3 in a row, number path,
Individualistic /
Teacher will use different interactive activities to develop addition and
Interactive activities include: 3 in a row, number path,
Individualistic /
word problems. Find unknown single digit number in
unknown number.
subtraction skills.
calculator game, guess my number.
Investigative
subtraction skills.
calculator game, guess my number.
Investigative
subtraction skills.
calculator game, guess my number.
Investigative
addition or subtraction equation.
• Teacher will use a fraction wall, measuring cups and fraction strips to explore
• Teacher will use a fraction wall, measuring cups and fraction strips to explore
• Teacher will use a fraction wall, measuring cups and fraction strips to explore
• Visualise the size of a fraction, through a number line ‐ a
• Visualise the size of a fraction, through a number line ‐ a
• Visualise the size of a fraction, through a number line ‐ a
Students will be able to use common fractions to
and explain ideas about a relationship between a part and a whole (part‐whole
Individualistic /
and explain ideas about a relationship between a part and a whole (part‐whole
Individualistic /
and explain ideas about a relationship between a part and a whole (part‐whole
Individualistic /
tool for representing and comparing fractions. Use words to
tool for representing and comparing fractions. Use words to
tool for representing and comparing fractions. Use words to
represent a part of a whole.
relationship).
Expositive
relationship).
Expositive
relationship).
Expositive
label the fractions.
label the fractions.
label the fractions.
• Teacher will encourage children to give real‐life examples when fractions are
• In groups, students will model a situation in which half,
• Students will receive a card set with the symbol, the words
• Fold a paper strip chocolate bar in half to make
useful.
third or fifth of the whole is being used. Students can draw,
Teacher will:
and various physical representations of 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4.
• Teacher will demonstrate various activities as described in the listed learning
demonstrate sharing halves. Use same strategy to partition
Students will be able to match the words, symbols and
• Teacher will give cards with the words ‘half’, ‘third’ and ‘fifth’ to different pairs
cut, and paste pictures, colour paper, write a story, etc.
• give each student a set of cards described under student activity.
• Students will arrange cards into sets representing one half,
activities.
kinder squares, play dough, pile of counters. Repeat for
Associative /
Performative /
Associative /
Add and subtract with whole digit numbers up to 1000
physical representations of one half, one quarter and
of students. Students will be asked to think of situations that explain what one
Students share ideas. Display work on wall and discuss with
• allocate time for students to make individual decisions.
one third and one quarter. Students need then to explain to
• Teacher will encourage children to give real‐life examples when fractions are
fourths: halve and halve again. Repeat spreading activity
Investigative
Investigative
Investigative
using knowledge of place value, properties of
one third.
half, one third and one fifth represent.
other pairs of students.
• organise students into pairs for discussion of decisions.
a partner why they made their choices.
useful.
with thirds on square bread slices.Spread a salada with
operations and relationship between addition and
• Teacher will organise a cooking session with students to follow a recipe in
• Students will follow recipes to cook different things in
• debrief with group to identify any remaining misconceptions.
• Students will make different physical representations of
D
vegemite. Discuss different fractional parts.
which they need to use 1/2, 1/3 and ¼
which they need to use 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4 of the ingredients.
these fractions.
subtraction. Represent and solve word problems
involving multiplication and division. Recognise
fractions (1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5) as a part of a whole.
Students solve addition and subtraction problems in groups
Students solve addition and subtraction problems in groups
Students solve addition and subtraction problems in groups
Students will be able to add and subtract 3 digit
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
using:
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
using:
• Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
using:
Associative /
Associative /
Associative /
numbers which include renaming (borrowing and
description, etc) addtion and subtraction of 3 digit numbers using counters and
• Counters, MAB
description, etc) addtion and subtraction of 3 digit numbers using counters and
• Counters, MAB
description, etc) addtion and subtraction of 3 digit numbers using counters and
• Counters, MAB
Expositive
Expositive
Expositive
trading).
MAB.
• Clipboard
MAB
• Clipboard
MAB
• Clipboard
• Game – (trading game with counters)
• Game – (trading game with counters)
• Game – (trading game with counters)
Students will be able to repeat addition as arrays,
Individualistic /
• Teacher will read arrays as a representation for multiplication. Introduce
• Students will model arrays using a range of concrete
Individualistic /
To read arrays as a representation for multiplication. Introduce symbols to
• Students will model arrays using a range of concrete
Individualistic /
using the language of multiplication like “by” and
Teacher will introduce symbols to represent arrays using visual illustrations.
Students use arrays as a representation for multiplication.
Expositive
symbols to represent arrays.
materials, exploring symbols to represent it.
Expositive
represent arrays.
materials, exploring symbols to represent it.
Expositive
“multiply”.
Students will be able to understand the commutative
Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
Students will represent multiplication by using concrete
Investigative /
Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
Students will represent multiplication by using concrete
Investigative /
Teacher will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory work
Students will represent multiplication by using concrete
Investigative /
property for multiplication.
description, etc) the use of arrays eg 3x4 and 4x3 to explain the relationship.
materials and grid paper.
Performative
description, etc) the use of arrays eg 3x4 and 4x3 to explain the relationship.
materials and grid paper.
Performative
description, etc) the use of arrays eg 3x4 and 4x3 to explain the relationship.
materials and grid paper.
Performative
Use properties of operations as strategies to multiply
and divide. Round numbers using the knowledge of
place value. Represent whole number on the number
• Students will explore the meaning of numerator and
Students wil:
• Students will explore the meaning of numerator and
line, find segment length and understand concept of
denominator using:
• complete paper folding activities with an emphasis on how
denominator using:
E
unit segment. Recognise unit fractions in both
‐ Paper folding activities
many equal parts are produced by the activity and how this
‐ Paper folding activities
• Teacher will illustrate the meaning of denominator and numerator using
• Teacher will lead paper folding activity emphasising the number of equal parts
• Teacher will illustrate the meaning of denominator and numerator using
‐ Make me 3/4
is recorded.
numerical and geometrical form (express area of a
Students will be able to understand the meaning
‐ Make me 3/4
concrete materials.
as naming the parts (denominator from the Latin meaning name).
concrete materials.
Individualistic /
‐ Sticky numbers
Individualistic /
• complete designated colour parts activity with an
Individualistic /
part of a shape as a fraction). Compare fractions with
attached to the numerator and denominator.
‐ Sticky numbers
• Teacher will ask students to investigate around the school environment where
• Teacher then will use paper folding outcomes to have students colour
same denominator or numerator. Describe and
• Teacher will ask students to work in groups using pre‐cut ‘tiles’ to explore the
Interrogative
Interrogative
emphasis on the number of equal parts coloured and how
Interrogative
fractions are displayed or can be used, analysing the meaning of numerator and
designated numbers of parts, the numerator (from Latin meaning count).
extend geometric and numeric patterns.
concept of denominator and numerator.
• Students look around the school environment to see
that is recorded.
• Students use pre‐cut ‘tiles’ (ex cut into 3,4,8 & 10 equal
denominator.
where fractions are displayed or can be used, to then
• choose a fraction and create it by paper folding and
pieces) They are asked to pick up 1 of the pieces and name
present these examples explaining the meaning of
present it to a partner who has to describe how to create
the piece. (Extend to multiple pieces).
numerator and denominator.
the name, in words and symbolically.
In groups, students will explore:
In groups, students will explore:
In groups, students will explore:
Teachers will let students explore equivalences and challenge them to explain
• partitioning a real object into halves, thirds and fifths
Teachers will let students explore equivalences and challenge them to explain
• partitioning a real object into halves, thirds and fifths
Teachers will let students explore equivalences and challenge them to explain
• partitioning a real object into halves, thirds and fifths
Students will be able to recognise equivalent
Associative /
Associative /
Associative /
the reasons for the equivalences (see learning activity)
• partitioning an identical object into sixths, eighths, ninths,
the reasons for the equivalences (see learning activity)
• partitioning an identical object into sixths, eighths, ninths,
the reasons for the equivalences (see learning activity)
• partitioning an identical object into sixths, eighths, ninths,
fractions.
Interrogative
Interrogative
Interrogative
tenths
tenths
tenths
• comparing the parts to discover equivalences
• comparing the parts to discover equivalences
• comparing the parts to discover equivalences
• Teacher will:
Represent fractions on number line. Recognise and
generate equivalent fractions (denominator 2, 3, 4, 6,
• Teachers will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory
In groups, students will:
• Teachers will model (personally, or by a video, a worksheet, a laboratory
In groups, students will:
‐ Oversee construction of fraction walls.
• Students create their own fraction wall.
8). Add and subtract fractions with same
Students will be able to add and subtract fractions
work description, etc) the addition and subtraction of fractions with concrete
• use concrete objects and diagrams to add and subtract
Expositive /
work description, etc) the addition and subtraction of fractions with concrete
• use concrete objects and diagrams to add and subtract
Expositive /
‐ Propose some problems for students to solve
Associative /
• Using the fraction wall students identify equivalent
denominator. Use decimal notation for fraction
with the same denominator.
objects and diagrams (the explanation should emphasize estimation and
fractions with the same denominator
Associative
objects and diagrams (the explanation should emphasize estimation and
fractions with the same denominator
Associative
‐ Encourage students to create and solve their own problems
Investigative
F
fractions.
judging the reasonableness of answers)
• evaluate the reasoneableness of the results obtained
judging the reasonableness of answers)
• evaluate the reasoneableness of the results obtained
‐ Place an emphasis on recording so that students can see the link between the
(convert between decimals and fractions). Use four
operations and their properties to solve word
conceptual idea and the mathematical recording of the problem”
problems; involving calculations with distances,
money and time.
• Using models and concrete objects, students will record
• Using models and concrete objects, students will record
• Using models and concrete objects, students will record
Following a progression of using models, words and then symbols, teacher will
the addition and subtraction of simple fractions through
Following a progression of using models, words and then symbols, teacher will
the addition and subtraction of simple fractions through
Following a progression of using models, words and then symbols, teacher will
the addition and subtraction of simple fractions through
Students will be able to use operations to solve
Expositive /
Expositive /
Expositive /
model the use of diagram to solve real life problems (including number lines,
demonstrating equivalence.
model the use of diagram to solve real life problems (including number lines,
demonstrating equivalence.
model the use of diagram to solve real life problems (including number lines,
demonstrating equivalence.
problems involving equivalent fractions.
Deliberative
Deliberative
Deliberative
fraction walls, collections) involving equivalent fractions.
e.g. ¼ is the same as 2/8
fraction walls, collections) involving equivalent fractions.
e.g. ¼ is the same as 2/8
fraction walls, collections) involving equivalent fractions.
e.g. ¼ is the same as 2/8
therefore ¼ + 1/8 is the same as 2/8 + 1/8 = 3/8
therefore ¼ + 1/8 is the same as 2/8 + 1/8 = 3/8
therefore ¼ + 1/8 is the same as 2/8 + 1/8 = 3/8
[list here]
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2








