Benzene: Aromatic Hydrocarbons Sheet Template
ADVERTISEMENT
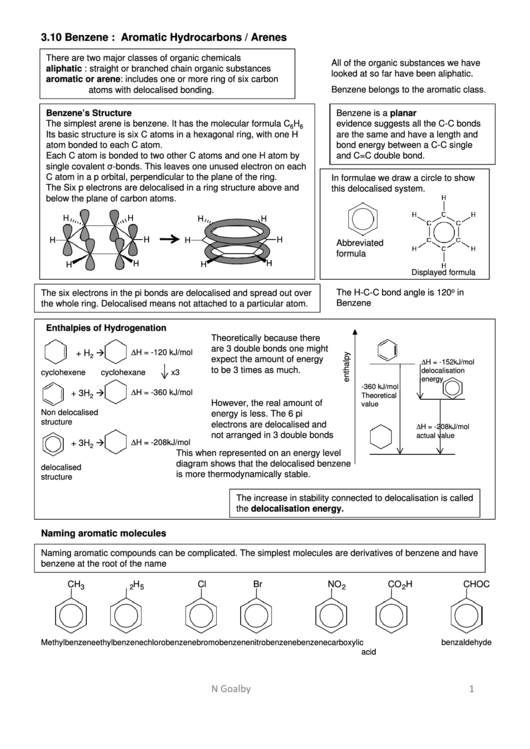
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
There are two major classes of organic chemicals
All of the organic substances we have
aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances
looked at so far have been aliphatic.
aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon
atoms with delocalised bonding.
Benzene belongs to the aromatic class.
Benzene’s Structure
Benzene is a planar molecule.The
The simplest arene is benzene. It has the molecular formula C
H
evidence suggests all the C-C bonds
6
6
Its basic structure is six C atoms in a hexagonal ring, with one H
are the same and have a length and
atom bonded to each C atom.
bond energy between a C-C single
Each C atom is bonded to two other C atoms and one H atom by
and C=C double bond.
single covalent σ-bonds. This leaves one unused electron on each
C atom in a p orbital, perpendicular to the plane of the ring.
In formulae we draw a circle to show
The Six p electrons are delocalised in a ring structure above and
this delocalised system.
below the plane of carbon atoms.
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Abbreviated
formula
H
H
H
H
Displayed formula
o
The H-C-C bond angle is 120
in
The six electrons in the pi bonds are delocalised and spread out over
Benzene
the whole ring. Delocalised means not attached to a particular atom.
Enthalpies of Hydrogenation
Theoretically because there
are 3 double bonds one might
∆H = -120 kJ/mol
+ H
2
expect the amount of energy
∆H = -152kJ/mol
to be 3 times as much.
delocalisation
cyclohexene
cyclohexane
x3
energy
-360 kJ/mol
∆H = -360 kJ/mol
+ 3H
Theoretical
2
However, the real amount of
value
Non delocalised
energy is less. The 6 pi
structure
electrons are delocalised and
∆H = -208kJ/mol
not arranged in 3 double bonds
actual value
∆H = -208kJ/mol
+ 3H
2
This when represented on an energy level
diagram shows that the delocalised benzene
delocalised
is more thermodynamically stable.
structure
The increase in stability connected to delocalisation is called
the delocalisation energy.
Naming aromatic molecules
Naming aromatic compounds can be complicated. The simplest molecules are derivatives of benzene and have
benzene at the root of the name
CH
C
H
Cl
Br
NO
CO
H
CHO
3
2
5
2
2
Methylbenzene
ethylbenzene
chlorobenzene
bromobenzene
nitrobenzene
benzenecarboxylic
benzaldehyde
acid
N Goalby
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2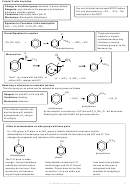 3
3 4
4