Staar Chemistry Quick Reference Guide
ADVERTISEMENT
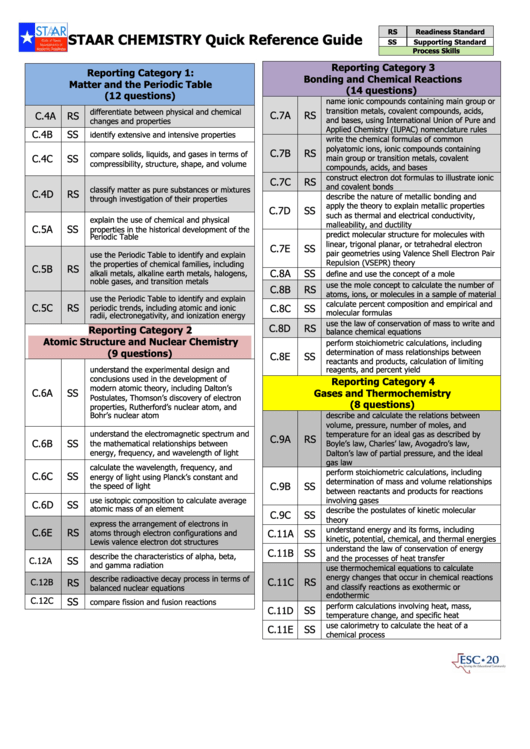
RS
Readiness Standard
STAAR CHEMISTRY Quick Reference Guide
SS
Supporting Standard
Process Skills
Reporting Category 3
Reporting Category 1:
Bonding and Chemical Reactions
Matter and the Periodic Table
(14 questions)
(12 questions)
name ionic compounds containing main group or
transition metals, covalent compounds, acids,
differentiate between physical and chemical
C.7A
RS
C.4A
RS
and bases, using International Union of Pure and
changes and properties
Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature rules
C.4B
SS
identify extensive and intensive properties
write the chemical formulas of common
polyatomic ions, ionic compounds containing
C.7B
RS
compare solids, liquids, and gases in terms of
C.4C
SS
main group or transition metals, covalent
compressibility, structure, shape, and volume
compounds, acids, and bases
construct electron dot formulas to illustrate ionic
C.7C
RS
and covalent bonds
classify matter as pure substances or mixtures
C.4D
RS
describe the nature of metallic bonding and
through investigation of their properties
apply the theory to explain metallic properties
C.7D
SS
such as thermal and electrical conductivity,
explain the use of chemical and physical
malleability, and ductility
C.5A
SS
properties in the historical development of the
predict molecular structure for molecules with
Periodic Table
linear, trigonal planar, or tetrahedral electron
C.7E
SS
pair geometries using Valence Shell Electron Pair
use the Periodic Table to identify and explain
Repulsion (VSEPR) theory
the properties of chemical families, including
C.5B
RS
C.8A
SS
alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens,
define and use the concept of a mole
noble gases, and transition metals
use the mole concept to calculate the number of
C.8B
RS
atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample of material
use the Periodic Table to identify and explain
calculate percent composition and empirical and
C.5C
RS
periodic trends, including atomic and ionic
C.8C
SS
molecular formulas
radii, electronegativity, and ionization energy
use the law of conservation of mass to write and
C.8D
RS
Reporting Category 2
balance chemical equations
Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
perform stoichiometric calculations, including
determination of mass relationships between
(9 questions)
C.8E
SS
reactants and products, calculation of limiting
understand the experimental design and
reagents, and percent yield
conclusions used in the development of
Reporting Category 4
modern atomic theory, including Dalton’s
C.6A
SS
Gases and Thermochemistry
Postulates, Thomson’s discovery of electron
(8 questions)
properties, Rutherford’s nuclear atom, and
describe and calculate the relations between
Bohr’s nuclear atom
volume, pressure, number of moles, and
understand the electromagnetic spectrum and
temperature for an ideal gas as described by
C.9A
RS
C.6B
SS
the mathematical relationships between
Boyle’s law, Charles’ law, Avogadro’s law,
energy, frequency, and wavelength of light
Dalton’s law of partial pressure, and the ideal
gas law
calculate the wavelength, frequency, and
perform stoichiometric calculations, including
C.6C
SS
energy of light using Planck’s constant and
determination of mass and volume relationships
C.9B
SS
the speed of light
between reactants and products for reactions
use isotopic composition to calculate average
involving gases
C.6D
SS
atomic mass of an element
describe the postulates of kinetic molecular
C.9C
SS
theory
express the arrangement of electrons in
understand energy and its forms, including
C.6E
RS
atoms through electron configurations and
C.11A
SS
kinetic, potential, chemical, and thermal energies
Lewis valence electron dot structures
understand the law of conservation of energy
C.11B
SS
describe the characteristics of alpha, beta,
and the processes of heat transfer
SS
C.12A
and gamma radiation
use thermochemical equations to calculate
energy changes that occur in chemical reactions
describe radioactive decay process in terms of
C.11C
RS
RS
C.12B
and classify reactions as exothermic or
balanced nuclear equations
endothermic
SS
C.12C
compare fission and fusion reactions
perform calculations involving heat, mass,
C.11D
SS
temperature change, and specific heat
use calorimetry to calculate the heat of a
C.11E
SS
chemical process
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2