Cell Structure Biology Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
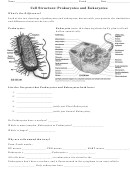
Cell Structure – Human
Structure
Basic Components of Cell:
cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional
a. cell membrane
- boundary
if its alive, must contain at least a single cell
b. cytoplasm (=cytosol)
the function of an organism is the summation of
– includes everything except
functions of its individual cells
cell membrane
cell first described 300 years ago by Robert Hook
c. nucleus
-genetic material
in human body
d. organelles & inclusions
internal structures
- highly organized, specialized
single fertilized egg ! 75–100 trillion cells (adult)
structures
[>10x’s more bacterial cells in body]
1. Cell Membrane
There are about 200 different kinds of cells in the
human body with a variety of sizes and shapes
defines boundary
human cells range in size from:
!phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol
eg. sperm cells are some of the smallest human cells
phospholipids have polar and nonpolar ends
eg. human eggs & fat cells are some of the largest, barely
tend to arrange themselves into double
visible to naked eye
layered films
eg. some nerve cells are 3 ft long (humans)
framework for all membranes of cells
while there is a great diversity in size and shape
!less diversity in function
help to provide a high capacity for self repair
in most:
proteins “float” randomly in this bilayer
= “fluid mosaic”
1
2
Microscopy , Cells, Tissues: Cell Structure – Animals/Humans; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2012.3
Microscopy , Cells, Tissues: Cell Structure – Animals/Humans; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2012.3
some membrane protein functions:
contains genetic material:
eg. receptors (ie. docking sites) for specific
genetic material
substances
eg. carriers: move specific solutes across
=chromosomes
membrane
100’s times length of cell
eg. enzymes: energy transforming enzymes
humans ~3’ of DNA/cell
the cell membrane is selectively permeable
4. Nucleolus
some things enter freely, some things cannot
cross or cross only with “help”
densely packed chromosome region within
nucleus
2. Cytoplasm (=Cytosol)
with proteins and ribosome precursors
contains mostly water, ions, organic molecules etc
site of RNA synthesis
variety of enzymes eg. glycolysis
important in formation of ribosomes
3. Nucleus
5. Mitochondria:
largest of internal cell structures
about size of small bacterial cell
number varies: one to many
contain their own set of DNA (genes):
in humans
passed only from mother to child
most cells have one nucleus
mtDNA remains unchanged generation after generation
RBC’s have none
except by slow random mutation
a few cells are multinucleate (2-50 nuclei)
! used as molecular clock to trace evolution of groups
surrounded by nuclear envelope
eg. all humans today descended from a single
same structure and cell membrane
woman of about 200,000 years ago =
mitochondrial EVE
3
4
Microscopy , Cells, Tissues: Cell Structure – Animals/Humans; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2012.3
Microscopy , Cells, Tissues: Cell Structure – Animals/Humans; Ziser Lecture Notes, 2012.3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4