Draft Data Validation Plan Review Form Page 28
ADVERTISEMENT
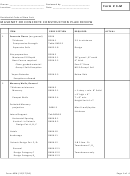
Draft Data Validation PRF-Tier II
Date: March 2, 2004
Page 28
Revision: 4.0
3.0
Cold Vapor AA Method for Mercury Data Review
3.5
Did the calibration curve for mercury possess a
correlation coefficient of greater than or equal to 0.995?
Action: If the correlation coefficient is less than 0.995, qualify all
positive data as “J,” and all non-detected compounds as “UJ.” If
the deviation is significant, data may be qualified as “R” based
upon professional judgement.
3.6
Were the Initial Calibration Verification (ICV) and the
Continuing Calibration Verification (CCV) analyzed with
the appropriate frequency?
Note: An Initial Calibration Verification (ICV) standard and a
blank must be analyzed after the initial calibration. This ICV
concentration should be near the mid-point of the working
range. The CCV standard is analyzed at a minimum frequency
of every 10 samples (10%) or every two hours. The CCV must
be analyzed at the beginning and end of an analytical.
3.7
Were the ICV and CCV within control limits (R) of 80% to
120%?
Note: Typically, ICV = 0.0025 ppm and CCV= 0.005 ppm.
Action: If the ICV or CCV %R is 65-79% or 121-135%, qualify all
positive results greater than the detection limit as “J.”
If the ICV or CCV %R are between 121-135%, results below the
detection limit are acceptable.
If the ICV or CCV %R is 65-79%, results below the detection limit
should be qualified as “UJ.”
If the ICV or CCV %R is less than 65%, qualify all positive results
as “R.”
If the ICV or CCV %R is greater than 135%, qualify all the results
greater than the detection limit as “R,” and results less than the
detection limit as acceptable.
3.8
Was the CCV standard analyzed at the beginning of the
run and also after the last analytical sample? A CCV
must also be analyzed after every tenth sample or every
two hours, whichever is more frequent.
Action: Note any discrepancies, and use professional judgement
along with other QA/QC information to qualify data.
3.9
Was the same CCV standard solution used throughout
the analytical runs for a sample delivery group of
samples received?
Action: If not, note any discrepancies, and use professional
judgement along with other QA/QC information to qualify data.
3.10
Was a blank analyzed after the ICV (also called the initial
calibration blank ICB), and the CCV (also called the
continuing calibration blank, CCB)?
Note: This blank confirms that carry over is not biasing the
next sample.
Action: If no blank was analyzed, qualify all positive data in the
next sample as “J.” All non-detected data is acceptable.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29