Kinematics - Cornell Notes Template
ADVERTISEMENT
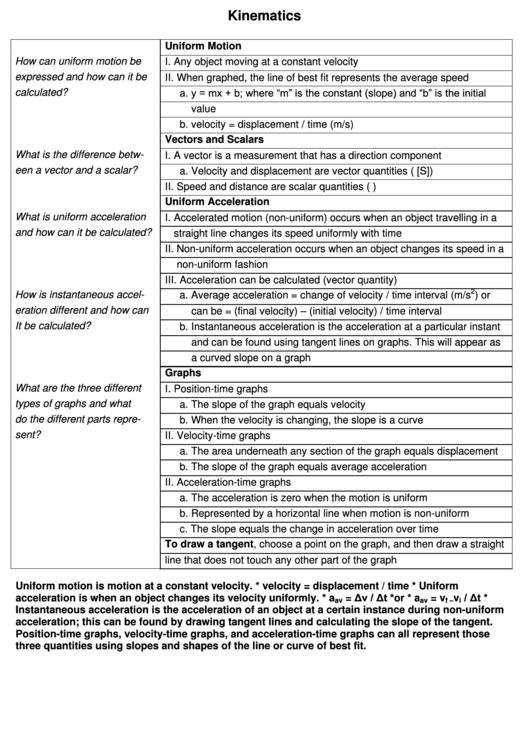
Kinematics
Uniform Motion
How can uniform motion be
I. Any object moving at a constant velocity
expressed and how can it be
II. When graphed, the line of best fit represents the average speed
a. y = mx + b; where “m” is the constant (slope) and “b” is the initial
calculated?
value
b. velocity = displacement / time (m/s)
Vectors and Scalars
What is the difference betw-
I. A vector is a measurement that has a direction component
een a vector and a scalar?
a. Velocity and displacement are vector quantities (e.g. 5 km/h [S])
II. Speed and distance are scalar quantities (e.g. 15 m away)
Uniform Acceleration
What is uniform acceleration
I. Accelerated motion (non-uniform) occurs when an object travelling in a
and how can it be calculated?
straight line changes its speed uniformly with time
II. Non-uniform acceleration occurs when an object changes its speed in a
non-uniform fashion
III. Acceleration can be calculated (vector quantity)
2
How is instantaneous accel-
a. Average acceleration = change of velocity / time interval (m/s
) or
can be = (final velocity) – (initial velocity) / time interval
eration different and how can
It be calculated?
b. Instantaneous acceleration is the acceleration at a particular instant
and can be found using tangent lines on graphs. This will appear as
a curved slope on a graph
Graphs
What are the three different
I. Position-time graphs
types of graphs and what
a. The slope of the graph equals velocity
do the different parts repre-
b. When the velocity is changing, the slope is a curve
sent?
II. Velocity-time graphs
a. The area underneath any section of the graph equals displacement
b. The slope of the graph equals average acceleration
II. Acceleration-time graphs
a. The acceleration is zero when the motion is uniform
b. Represented by a horizontal line when motion is non-uniform
c. The slope equals the change in acceleration over time
To draw a tangent, choose a point on the graph, and then draw a straight
line that does not touch any other part of the graph
Uniform motion is motion at a constant velocity. * velocity = displacement / time * Uniform
= Δv / Δt * or * a
/ Δt *
acceleration is when an object changes its velocity uniformly. * a
= v
v
f –
av
av
i
Instantaneous acceleration is the acceleration of an object at a certain instance during non-uniform
acceleration; this can be found by drawing tangent lines and calculating the slope of the tangent.
Position-time graphs, velocity-time graphs, and acceleration-time graphs can all represent those
three quantities using slopes and shapes of the line or curve of best fit.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Miscellaneous
 1
1 2
2 3
3