Transition Metals General Features
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u i d e – q u e s t i o n s
TRANSITION METALS: GENERAL FEATURES
1. a) Write the electronic structure of the following transition metal atoms using the short form in
which, for example, Co would be [Ar]3d
7
4s
2
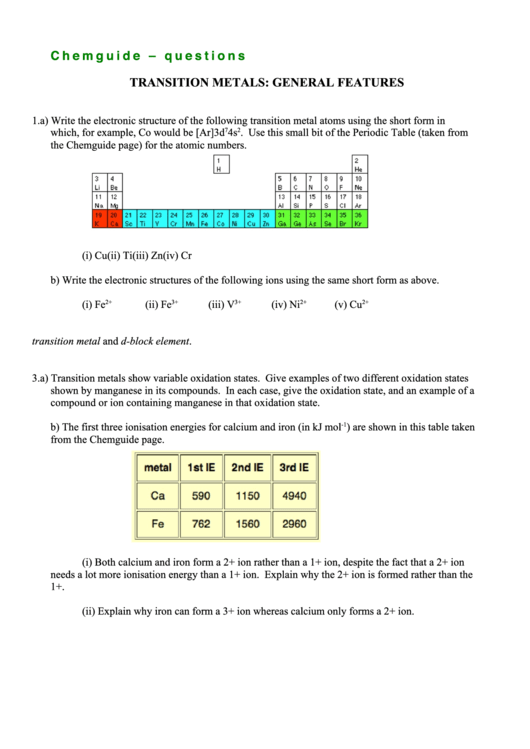
. Use this small bit of the Periodic Table (taken from
the Chemguide page) for the atomic numbers.
(i) Cu
(ii) Ti
(iii) Zn
(iv) Cr
b) Write the electronic structures of the following ions using the same short form as above.
(i) Fe
2+
(ii) Fe
3+
(iii) V
3+
(iv) Ni
2+
(v) Cu
2+
2. Explain the difference between the terms transition metal and d-block element.
3. a) Transition metals show variable oxidation states. Give examples of two different oxidation states
shown by manganese in its compounds. In each case, give the oxidation state, and an example of a
compound or ion containing manganese in that oxidation state.
b) The first three ionisation energies for calcium and iron (in kJ mol
-1
) are shown in this table taken
from the Chemguide page.
(i) Both calcium and iron form a 2+ ion rather than a 1+ ion, despite the fact that a 2+ ion
needs a lot more ionisation energy than a 1+ ion. Explain why the 2+ ion is formed rather than the
1+.
(ii) Explain why iron can form a 3+ ion whereas calcium only forms a 2+ ion.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








