Lightalarms Wire Size Guide
ADVERTISEMENT
Wire Size Guide
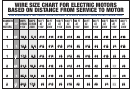
DETERMINING WIRE SIZE
The following information is provided to assist in designing proper emergency lighting systems effectively and economically by using the smallest permissible wire
size for load circuits. When remote lighting fixtures and/or exit signs are connected to emergency lighting units, circuit runs must be of sufficient size to maintain
a proper operating voltage to all lamps. The National Electrical Code limits voltage to drop to a maximum of 5% of nominal. The table below gives the maximum
length or wire run based on systems voltage, wire gauge and total wattage on the run. To determine the maximum length of a wire run not listed, divide the
value of the load in watts into the constant listed at the bottom of each row. Example, the maximum wire run for #10 wire on a 12 volt system, with a 54 watt load,
is 3397 ÷ 54 or 62 feet.
Conversely, to determine the maximum load on a run of known length, divide the length into the constant. Example, a 36 foot run of #12 wire on a 6 volt systems
can be loaded to, 534 ÷ 36, or 14 watts; on #10 wire, 23 watts.
WIRING DISTANCE IN FEET (Maximum Voltage Drop 5%)
6 volt wire size
12 volt wire size
24 volt wire size
Total watts
on wire run
#12
#10
#8
#6
#12
#10
#8
#6
#4
#12
#10
#8
#6
89
141
225
357
356
566
900
1431
+
1425
+
+
+
6
8
66
106
168
268
267
424
675
1073
1707
1068
1698
+
+
59
94
150
238
237
377
600
954
1517
949
1509
+
+
9
53
84
135
214
213
339
540
859
1366
854
1358
+
+
10
12
44
70
112
178
178
283
450
715
1138
712
1132
1801
+
33
53
84
134
133
212
337
536
853
534
849
1350
+
16
29
47
75
119
118
188
300
477
758
474
754
1200
1909
18
24
22
35
56
89
89
141
225
357
569
356
566
900
1431
21
33
54
85
85
135
216
343
546
341
543
864
1374
25
19
31
50
79
79
125
200
318
505
316
503
800
1272
27
17
28
45
71
71
113
180
286
455
284
452
720
1145
30
14
23
37
59
59
94
150
238
379
237
377
600
954
36
12
20
32
51
50
80
128
204
325
203
323
514
818
42
11
18
30
47
47
75
120
190
303
189
301
480
763
45
11
17
28
44
44
70
112
178
284
178
283
450
715
48
10
16
27
42
42
67
108
171
273
170
271
432
687
50
7
11
18
28
28
45
72
114
182
113
181
288
458
75
5
8
13
21
21
33
54
85
136
85
135
216
343
100
150
-
5
9
14
14
22
36
57
91
56
90
144
229
-
-
6
10
10
16
27
42
68
42
67
108
171
200
-
-
5
8
8
13
21
34
54
34
54
86
137
250
300
-
-
-
7
7
11
18
28
45
28
45
72
114
-
-
-
5
5
8
13
21
34
21
33
54
85
400
-
-
-
-
-
6
10
17
27
17
27
43
68
500
534
849
1350
2148
2137
3397
5403
8590
13660
8548
13588
21613
34363
Constant
Longer Wire Runs
For example, a 36 foot long, 6 volt circuit has (3) 9 watt heads spaced 12 feet
The wiring distances give the maximum length of a battery circuit, assuming that
apart. According to the wire run table, # 8 wire must be used
the entire load is concentrated at the end of the circuit. If loads are uniformly
(at 50 feet for a 5% voltage drop.) but, by multiplying the 31 feet for #10 wire by
spaced along the circuit path (equal watts, equal distances), the lengths in the
1.5, a 46 1/2 foot wire run is acceptable, so #10 wire may be used and still meet
table may be increased, based on number of fixtures on a given circuit, by
the 5% voltage drop limitation.
means of the chart and formula below.
Note: According to the National Electrical Code, Article 720-Y, the smallest
2
3
4
5
6
N
Number of Fixtures
permissible wire size for systems under 50 volts is the #12 wire gauge.
1.33
1.5
1.6
1.67
1.71
2n/(n+1)
Multiply By Feet
114
Accessories and General Information Section
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1