Chemistry Worksheets
ADVERTISEMENT
Chemistry
Chapter 2
Chapter Outline
•
Atoms
•
Ions
•
Chemical Bonds
•
pH scale
•
Water
•
Carbohydrates
•
Lipids
•
Proteins
•
Nucleic Acids – DNA and RNA
Atoms and Ions
•
All matter is formed of Atoms.
•
Each atom has protons and neutrons in nucleus.
•
Protons are positively charged particles.
•
Neutrons are neutral particles.
•
Nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of electrons.
•
Electrons are negatively charged particles.
•
Ions have different # of protons and electrons.
Human Body and Elements
•
Human body has 24 elements
•
Elements have only 1 type of atoms.
•
Major Elements – 99.3%
H, O, C and N
•
Mineral Elements – 0.7%
•
Trace Elements – less than 0.01%
Importance of # of atomic particles
•
Atomic Number: # of protons determine the element; 1 = H, 6 = C, 7 = N and so on.
•
Mass Number is equal to # of protons + # of neutrons
12
14
•
# of neutrons determine the isotope; C
is the most common carbon and has 6 p + 6 n but C
has 6 p + 8 n and is radioactive.
•
# of electrons in outer shell determines chemical behavior of a molecule. # of covalent bonds made by H = 1, O = 2, N = 3, C =
4 and P = 5
Chemical Bonds
•
Atoms interact to form molecules. 3 basic type of interactions between atoms are:
•
Covalent bonds
•
Ionic bonds
•
Hydrogen bonds
Covalent Bonds
•
Covalent bonds: Atoms form share electron pair to form covalent bond.
•
Unequal sharing of electrons result in Polar molecules. Equal sharing of electrons result in non-polar molecules.
•
Very strong bonds.
•
Non-polar molecule Methane = CH
4
•
Polar molecules: water = H
O, and ammonia = NH
2
3
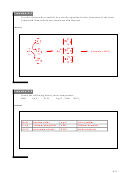
Ionic Bonds
•
Atoms change into ions by complete transfer of electron/s.
•
A positive ion and a negative ion attract each other and form ionic bond.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3