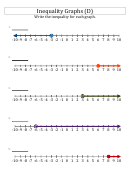
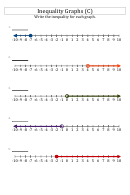
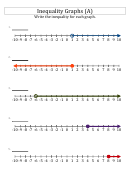
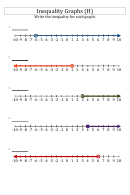
Useful Inequalities
ADVERTISEMENT
√
√
n
n
n
n
Useful Inequalities
n
n
n
n
2
1/(12n+1)
1/12n
´
´
´
´
{x
Stirling
e
≤
2πn
e
≤ n! ≤
2πn
e
≤ en
0}
e
e
e
e
version 0.10a · August 1, 2011
3
3
√
x
x cos x
x
x
3
trigonometric
x
≤ x cos x ≤
≤ x
cos x ≤ x
≤ x cos
√
≤ sin x ≤
2
n
n
n
!
!
!
2
2
1
x
/3
6
3
X
X
X
2
2
Cauchy-Schwarz
x
y
≤
x
y
i
i
3
i
i
x
2
π
ˆ
˜
x cos(0.56 x) ≤ x ≤ x +
≤ tan x,
and
x ≤ sin x,
for x ∈
0,
.
i=1
i=1
i=1
2
3
π
1
1
1
n
!
n
!
n
!
2
p
p
p
x
/2+αx
hyperbolic
cosh(x) + α sinh(x) ≤ e
,
where x ∈ R, α ∈ [ 1, 1].
X
p
X
p
X
p
Minkowski
|x
+ y
|
≤
|x
|
+
|y
|
,
for p ≥ 1.
i
i
i
i
i=1
i=1
i=1
√
a + b
b
a
Napier
b >
>
>
ab > a,
for 0 < a < b.
1/p
1/q
2
ln(b)
ln(a)
n
n
!
n
!
1
1
X
X
p
X
q
H¨ o lder
|x
y
| ≤
|x
|
|y
|
,
for p, q > 1,
+
= 1.
i
i
i
i
p
q
s P
i=1
i=1
i=1
2
P
x
x
1/n
n
“ Y
”
i
i
max{x
} ≥
≥
≥
x
≥
≥ min{x
}
means
i
i
i
1
r
n
n
P
x
Bernoulli
(1 + x)
≥ 1 + rx,
for x >
1, r ∈ R \ (0, 1). If r = 2n (n ∈ N),
i
inequality holds for x ∈ R. Reverse holds for x >
1, r ∈ [0, 1].
r
s
M
≤ M
,
for all pairs r ≤ s, where:
power means
w
w
rx
1
1/r
r
(1 + x)
≤ 1 +
,
for r > 1,
1 ≤ x <
.
n
!
1
(r
1)x
r
1
X
r
r
P
M
(x
, x
, . . . , x
) =
w
x
and
w
= 1.
1
2
n
i
i
w
i
x
i=1
n
x
´
e
≥ 1 +
≥ 1 + x,
for x ∈ R, n > 0 (left), n ≥ 1 (right).
exponential
r
If r =
∞, 0, +∞, M
tends to min, geom. mean and max, respectively.
n
w
If x < 0, then n ≥
x is required for both. Outer inequality always holds.
p
k
(k+1)
p
S
≥
S
,
for 1 ≤ k < n, where:
Maclaurin
k
k+1
2
x
x
e
x
e
≥ x
, for x ∈ R,
e
≥ 1 + x +
, for x ≥ 0, reverse for x ≤ 0.
1
X
2
S
=
a
a
· · · a
,
and
a
> 0.
i
i
i
i
k
n
´
1
2
k
k
1≤i
<···<i
2
3
≤n
x
x
x
1
k
˘
¯
logarithm
≤ log(1 + x) ≤ min
x, x
+
,
for x >
1.
x + 1
2
3
2
Newton
S
≥ S
S
,
for 1 ≤ k < n, and S
as before.
k
k 1
k+1
k
2x
x
≤ log(1 + x) ≤
√
,
for x ≥ 0. Reverse for x ∈ ( 1, 0].
2 + x
x + 1
Jensen
ϕ (E [X]) ≤ E [ϕ(X)],
where X is a random variable, and ϕ convex.
2
3
x
x
For concave ϕ the reverse holds. Without probabilities:
log(1 + x) ≥ x
+
,
for x ∈ [0, ∼ 0.45], reverse elsewhere.
2
4
n
n
X
X
´
2
3
ϕ
p
x
≤
p
ϕ (x
),
where p
≥ 0,
P
p
= 1.
x
x
i
i
i
i
i
i
log(1
x) ≥
x
,
for x ∈ [0, ∼ 0.43], reverse elsewhere.
i=1
i=1
2
2
n
n
n
n
n
1
X
X
X
X
´
´
X
Chebyshev
f (a
)g(b
)p
≥
f (a
)p
g(b
)p
≥
f (a
)g(b
)p
,
log(n + 1) ≤
≤ log(n) + 1
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
n i+1
i
harmonic
i
i=1
i=1
i=1
i=1
i=1
P
for a
≤ · · · ≤ a
, b
≤ · · · ≤ b
, and f, g nondecreasing, p
≥ 0,
p
= 1.
1
n
1
n
i
i
√
√
√
1
√
2
x + 1
2
x <
< 2
x
2
x
1,
for x ≥ 1.
square root
√
ˆ
˜
ˆ
˜
ˆ
˜
With expectations: E
f (X)g(X)
≥ E
f (X)
E
g(X)
.
x
n
n
n
k
n
“ n
n
en
k
”
k
X
X
X
´
´
a
b
≥
a
b
≥
a
b
,
for a
≤ · · · ≤ a
,
≤
≤
≤
,
for n ≥ k > 0.
rearrangement
binomial
1
n
i
i
i
π(i)
i
n i+1
k
k
k!
k
i=1
i=1
i=1
b
≤ · · · ≤ b
and π a permutation of [n]. More generally:
d
1
n
“ n
”
X
d
binomial sum
≤ n
+ 1,
for n ≥ d ≥ 0,
n
n
n
i
X
X
X
f
(b
) ≥
f
(b
) ≥
f
(b
),
i=0
i
i
i
π(i)
i
n i+1
d
i=1
i=1
i=1
“ n
en
”
d
X
´
≤
,
for n ≥ d ≥ 1.
´
with f
(x)
f
(x)
nondecreasing for all 1 ≤ i < n.
i+1
i
i
d
i=0
p
q
x
y
1
1
Young
xy ≤
+
,
for x, y ≥ 0 and p, q > 0 ,
+
= 1.
2n
2n
2
“ 2n
2
”
p
q
p
q
≤
≤
√
middle binomial
√
2
n
n
2n
n
n
n
a
i
X
Y
Y
a
a
n
Chong
≥ n,
and
a
≥
a
,
for a
> 0.
n
i
π(i)
´
ˆ
α
(1 α)
˜
≤
α
(1
α)
,
for α ∈ (0, 1).
i
i
i
binomial ratio
a
αn
π(i)
i=1
i=1
i=1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3