9 4 Polar Form Of A Linear Equation
ADVERTISEMENT
9.4
Polar Form of a Linear Equation
date _______
Goal: ______________________________________________________________________________
3
+
=
= −
+ ) on a polar graph is impossible because you have
y
x
Graphing 3
x
2
y
6
(or the equivalent
3
2
( )
r θ
rectangular coordinates (x,y) instead of polar coordinates
,
. Therefore, we rewrite linear equations using
polar coordinates (also known as “polar form”).
l
The polar form of an equation for a line
is closely related to the normal form. From the normal form,
we can easily identify the polar form.
Normal: starting at the origin, a line perpendicular to the given line
φ
φ
+
−
=
x
y
p
Normal Form:
cos
sin
0
φ
Note:
is the positive angle between the positive x-axis and the normal
(
)
θ φ
=
−
p
r
Polar Form of a Linear Equation:
cos
φ
** choose the value of
according to the quadrant in which the normal lies **
−
c
B
θ
φ
p φ
=
=
Note:
r
,
are variables and
,
are constants that we have to find …
p
and
Arc
tan
A
+
2
2
A
B
+
=
x
y
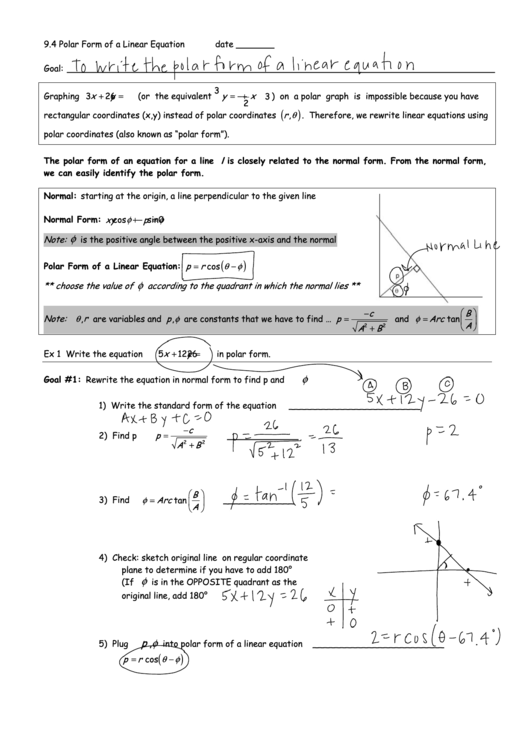
Ex 1
Write the equation 5
12
26
in polar form.
φ
Goal #1:
Rewrite the equation in normal form to find p and
1)
Write the standard form of the equation
________________________
−
c
=
p
2)
Find p
_____________
+
2
2
A
B
B
φ
=
3)
Find
Arc
tan
_____________
A
4)
Check: sketch original line on regular coordinate
plane to determine if you have to add 180°
φ
(If
is in the OPPOSITE quadrant as the
original line, add 180°
p φ
,
5)
Plug
into polar form of a linear equation
________________________
(
)
θ φ
=
−
p
r
cos
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3