Family Relationship Chart Sample Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
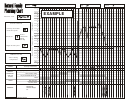
This chart shows the blood relationship of “YOU” to
YOU. Those above YOU on the chart are “ascendant”
everyone else on the chart.
cousins, those below YOU are “descendant” cousins.
1. In-laws are relatives YOU gain when YOU or your
8. BOB is four steps from YOUR common ancestor whereas
siblings marry. A half-brother or a half-sister is someone
YOU are only three steps away. YOU are closer to the
who shares just one parent with YOU. These relationships
common ancestors who are YOUR g-grand-parents. They
are not illustrated in this chart.
are BOB’s g-g-grandparents. Count the ‘g’s in the closest
relationship which in this case is 2. So he is a second
2. The siblings of YOUR grandparents are your granduncle
cousin but one generation removed from (below) YOU.
or grandaunt, not great uncle nor great aunt. Similarly, the
That makes him YOUR descendant 2C1R.
siblings of YOUR great-grandparents are YOUR great-
granduncle or great-grandaunt. Also the same nomen-
9. SUE is two steps from your common ancestor whereas
clature is used for grandnephew and grandniece.
YOU are four steps away. SUE is the closest to the
common ancestors who are her grandparents. One ‘g’
3. Cousins are persons who are related through a sibling of
makes her a first cousin two generations removed from
one of YOUR ancestors. YOU and a cousin will share one
YOU. She is YOUR grandmother’s first cousin. Since YOU
or more ancestors. There is no such thing as a half-cousin.
are two generations below SUE, YOU and SUE are 1C2R.
4. To determine a cousin relationship, first locate the nearest
common ancestor(s). Count the number of generations
10. Watch out for titled relatives who may not be whom they
(steps) up for each person to the common ancestor.
seem to be. An “aunt” may actually be a grandaunt or a
cousin and “Grandmaw” may actually be a great-grand-
5. If the number of steps between each person and the
mother. Misunderstanding of the ancestor hierarchy is
common ancestor is the same, count the number of ‘g’s in
often a problem.
the common ancestor’s title. For instance, first cousins
share the same grandfather or grandmother or both. There
11. Some people may have a relative title but they may not
is one ‘g’ in grandfather and grandmother, so that makes
be related. Some are religious titles (Father, Sister, etc.)
them first cousins to each other.
Others may be given the title by everyone, not just
relatives.
6. Second cousins share the same great-grandparent(s), so
two ‘g’s yields second cousins. It is similarly done for
12. YOU may be related in more than one way with another
more distant common ancestors.
person because of a marriage between relatives in an
7. If the number of steps between each person and the
earlier generation. That creates more than one pathway to
common ancestor is different, they are removed cousins,
the common ancestor.
meaning they are one or more generations above or below
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1 2
2