Core 40 End-Of-Course Assessment Algebra Reference Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
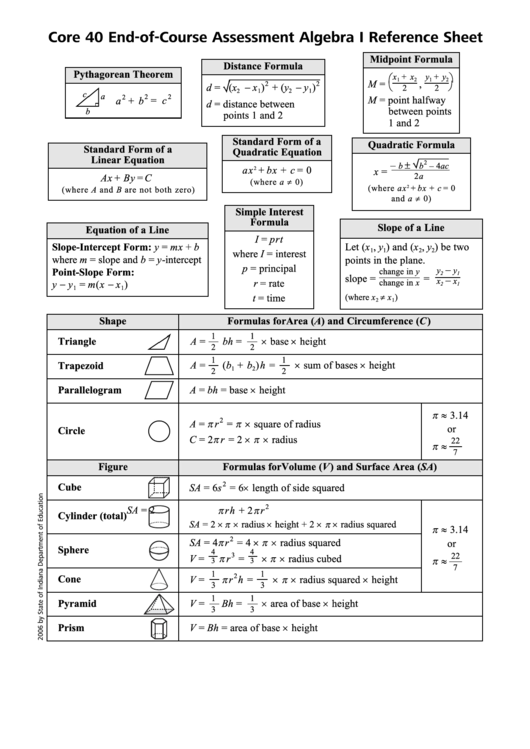
Core 40 End-of-Course Assessment Algebra I Reference Sheet
Midpoint Formula
Distance Formula
Pythagorean Theorem
⎞
⎛
x
+ x
y
+ y
1
2
1
2
M =
,
⎠
− x
− y
⎝
2
2
d = (x
)
+ ( y
)
2
2
2
1
2
1
c
a
2
2
2
M = point halfway
a
+ b
= c
d = distance between
between points
b
points 1 and 2
1 and 2
Standard Form of a
Quadratic Formula
Standard Form of a
Quadratic Equation
Linear Equation
±
2
–
b
b
– 4ac
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0
x =
2a
Ax + By = C
(where a ≠ 0)
(where ax
2
+ bx + c = 0
(where A and B are not both zero)
and a ≠ 0)
Simple Interest
Formula
Slope of a Line
Equation of a Line
I = prt
Let (x
, y
) and (x
, y
) be two
Slope -Intercept Form: y = mx + b
1
1
2
2
where I = interest
where m = slope and b = y-intercept
points in the plane.
−
p = principal
y
y
change in y
Point-Slope Form:
2
1
−
slope =
=
y − y
= m(x − x
x
x
r = rate
change in x
)
2
1
1
1
≠ x
(where x
)
t = time
2
1
Shape
Formulas for Area (A) and Circumference (C )
1
1
× base × height
A =
bh =
Triangle
2
2
1
1
× sum of bases × height
A =
(b
+ b
) h =
Trapezoid
1
2
2
2
A = bh = base × height
Parallelogram
π ≈ 3.14
A = π r
= π × square of radius
2
or
Circle
C = 2 π r = 2 × π × radius
22
π ≈
7
Figure
Formulas for Volume (V ) and Surface Area (SA)
2
= 6 × length of side squared
Cube
SA = 6s
SA = 2 π rh + 2 π r
2
Cylinder (total)
SA = 2 × π × radius × height + 2 × π × radius squared
π ≈ 3.14
SA = 4 π r
= 4 × π × radius squared
2
or
Sphere
4
4
π r
× π × radius cubed
3
22
π ≈
V =
=
3
3
7
1
1
π r
× π × radius squared × height
2
Cone
V =
h =
3
3
1
1
× area of base × height
V =
Bh =
Pyramid
3
3
V = Bh = area of base × height
Prism
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1