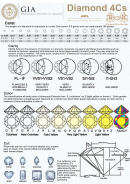
Diamond Fundamentals Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
Diamond Fundamentals 101
This guide is intended for an audience that is not familiar with the basics of diamonds. We will
be discussing carat weight, cut, color, clarity, in addition to some details regarding gemological
labs and their importance in diamond grading.
Carat Weight
Carat “weight” is actually a misnomer. It is more appropriate to describe a carat as a unit of
mass. A carat is equal to exactly 200 mg (milligrams) or 0.2 grams and is used to describe the
weights exactly 600 mg – which is quite heavy
mass of gemstones and pearls. So, a
3 carat stone
for a gemstone if you think about it! Keep in mind that although higher carat stones fetch more
value, it does not necessarily mean they are of better quality than smaller stones. Obviously, if a
piece of jewelry is comprised of a higher weight of gold, it will cost more. So higher carat stones
add value, but the beauty and downside of diamonds is that their production process in nature is
completely random. That is why a smaller stone can possibly be produced in more favorable
conditions to have better color and clarity. Diamonds can also be produced in a laboratory but
that is a separate topic in itself. All in all, think carat = mass.
Color
We are going to discuss color by two different standards. Firstly, in an ideal world, a chemically
pure diamond would not consist of any color. Like anything else in life, diamonds aren’t perfect.
A diamond’s color can either add or detract from its value. For example, if a diamond has a
detectable yellow color, it may be discounted, while pink or red diamonds could fetch a high
value because of how rare they are. When most people think of a diamond, they think of a white
stone, but diamonds can actually be almost any color like yellow, orange, red, blue, or even
black.
In terms of diamond grading, color is thought of a little differently.
Diamond gemstones
that are
used in engagement rings are described by a variety of commonly accepted adjectives that
categorize their tier. For example, the rarest diamonds appear totally or almost colorless. Fancy
color diamonds are most commonly yellow or brown. Pale yellow diamonds to brown in color
are categorized within the normal color range. The normal color range diamonds are the ones
that are graded on a scale of D – Z. Here we’ll go more into detail about what all these letters
mean.
Keep in mind that different labs use different standards to describe diamond color but these are
the most commonly accepted:
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4