Potential & Kinetic Energy Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
and earth (earthquake or seismic) or water, are also examples of mechanical
kinetic energy. The amount of kinetic energy contained in a moving object
depends on its speed and its mass.
If the motion is of electrons moving through a conductor, it is electrical kinetic
energy.
If the motion is the random vibration of atoms and molecules, it is thermal
kinetic energy.
Electromagnetic waves, which do not require matter to carry energy, are also
kinetic energy, because they move and can cause change or work.
Potential energy is stored energy, not presently doing work or causing change.
For mechanical potential energy, the energy is stored because of the object’s
position above the ground (gravitational potential energy) or the object’s
internal stress condition (elastic potential energy). Water stored behind a
high dam, which must flow downhill because of the pull of gravity, is an example
of gravitational potential energy. A stretched rubber band and compressed
spring are two examples of elastic potential energy. Deformed rock along a
fault line, which when released causes an earthquake, is another example of
elastic potential energy.
Chemical energy and nuclear energy are both forms of potential energy,
because both store energy that is not presently doing work. In chemical energy,
it is the bonds between atoms that store the energy. In nuclear energy, it the
force that holds the atomic nucleus together that stores the energy. Only when
chemical or nuclear energy is transformed into thermal or electromagnetic
energy do they become kinetic.
If electric charges are not moving (they are “static”), the electrical energy is
potential. A capacitor is an electrical device that directly stores electrical
charges without converting it into another form.
Electromagnetic waves move at a very fast constant speed (the “speed of
light”), and thus can only be kinetic, not potential, energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be destroyed, but
only transformed into different forms. The motion of objects can result in the
conversion of mechanical energy from potential to kinetic, sometimes in a regular
cycle. Mechanical energy is usually transformed into thermal energy by friction (a
force that opposes motion).
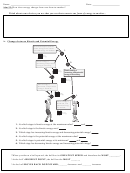
In a roller coaster, potential energy is first stored in the car when it is pulled to the
top of the highest hill of the roller coaster. When the car is released and increases
its speed down the track, pulled by gravity, the potential energy is reduced as the
car moves lower, but the kinetic energy increases as the car’s speed increases.
When the car reaches the bottom of the first hill, and begins to climb the second
hill, the kinetic energy of the car is transformed back to potential energy, as the car
climbs to a higher position but slows due to the pull of gravity. Eventually the car
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4